SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:分析血清 B 型脑钠肽(BNP) 、降钙素原(PCT) 、超敏 C 反应蛋白(hs-CRP)水平与重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患 者心功能分级的相关性。方法: 选取 2019 年 1 月至 2021 年 2 月该院收治的 100 例重症肺炎患者为研究对象,依据是否合并心力衰竭将 其分为单纯组 47 例和合并组 53 例,另选取同期本院 50 名健康体检者为对照组。比较三组血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平,依据美国心脏 病协会(NYHA)心功能分级标准,比较合并组不同心功能分级患者血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平,采用 Pearson 相关性分析血清 BNP、 PCT、hs-CRP 水平与重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者心功能分级的相关性。 结果: 合并组血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平均高于单纯组和对照组, 且单纯组高于对照组, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05) ; 合并组心功能分级Ⅳ级患者血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平均高于Ⅱ级和Ⅲ级, 且Ⅲ 级高于Ⅱ级,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Pearson 相关性分析结果显示, 血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平与重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者 心功能分级呈正相关( r>0. P<0.05)。 结论: 重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平升高,且与患者心功能分级呈正 相关。
【关键词】 重症肺炎,心力衰竭,血清 B 型脑钠肽,降钙素原,超敏 C 反应蛋白,相关性
Correlations among serum BNP, PCT, hs-CRP levels and cardiac function classification in patients with severe pneumonia complicated with heart failure
PENG Lili, PEI Suli, SONG Li
(Department of Respiratory Medicine of Nanjing Red Cross Hospital, Nanjing 210000 Jiangsu, China)
【 Abstract 】 Objective: To analyze correlations among serum B-type brain natriuretic peptide (BNP), procalcitonin (PCT), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels and cardiac function classification in patients with severe pneumonia complicated with heart failure. Methods: 100 patients with severe pneumonia admitted to the hospital from January 2019 to February 2021 were selected as the research objects. According to whether the patients had heart failure, they were divided into simple group (47 cases) and combined group (53 cases). Another 50 healthy subjects were selected as the control group. The levels of serum BNP, PCT and hs-CRP were compared among the three groups. According to the American Heart Association (NYHA) cardiac function classification standard, the serum BNP, PCT and hs-CRP levels of the patients with different cardiac function classifications in the combined group were compared. Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlations among the serum BNP, PCT, hs-CRP levels and the cardiac function classification in the patients with severe pneumonia complicated with heart failure. Results: The levels of serum BNP, PCT and hs-CRP in the combined group were higher than those in the control group and the simple group, and the simple group was higher than the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The levels of serum BNP, PCT and hs-CRP in the patients with cardiac function classification IV in the combined group were higher than those in the patients with classification II and classification III, those in the patients with classification III were higher than those in the patients with classification II, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that serum BNP, PCT and hs-CRP levels were positively correlated with the cardiac function classification in the patients with severe pneumonia complicated with heart failure (r>0. P<0.05). Conclusions: The levels of the serum BNP, PCT and hs-CRP in the patients with severe pneumonia complicated with heart failure are increased, and their levels are positively correlated with the cardiac function classification.
【Keywords】 Severe pneumonia; Heart failure; Serum B-type brain natriuretic peptide; Procalcitonin; Hypersensitive C-reactive protein;Correlation
重症肺炎患者病情进展急速,可导致脏器功能衰竭。心力衰竭是重症肺炎常见的合并症,主要由 炎症导致肺功能损伤,引起气体交换障碍,导致心 肺之间血氧流通受阻,心脏缺血、缺氧引起心力衰 竭 [1] 。因此,早期诊断重症肺炎患者合并心力衰竭 的严重程度,对改善患者预后至关重要。血清 B 型 脑钠肽(BNP)是反映心力衰竭程度的重要指标。
降钙素原(PCT)能够敏感地反映感染与炎症的严 重程度。超敏 C 反应蛋白(hs-CRP)是反映全身 性感染的非特异性标志物,也是心血管不良事件的 有效预测因子 [2]。本文分析血清 BNP、PCT、hs- CRP 水平与重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者心功能分级 的相关性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2019 年 1 月至 2021 年 2 月 本院收治的 100 例重症肺炎患者为研究对象。纳入 标准:符合《中国成人医院获得性肺炎与呼吸机相 关性肺炎诊断和治疗指南(2018 年版) 》中重症 肺炎诊断标准 [3] ;经胸部 X 线检查确诊;血气分析 提示低氧血症;自愿参与本研究;临床资料完整。 排除标准:合并恶性肿瘤;合并严重肝、肾等脏器 功能不全;近 3 个月内服用相关药物治疗;妊娠或 哺乳期; 精神障碍。参照美国心脏病协会(NYHA) 心功能分级,依据是否合并心力衰竭将其分为单纯 组 47 例和合并组 53 例。单纯组:男 25 例,女 22 例; 年 龄 21~76 岁, 平 均(51.65±7.32) 岁。 合 并 组: 男 28 例, 女 25 例; 年 龄 20~79 岁, 平 均 (52.42±7.28) 岁。另选取同期本院 50 名健康体 检者为对照组。对照组:男 30 名,女 20 名;年龄 20~78 岁, 平均(51.83±7.17) 岁。三组一般资料 比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),有可比性。 1.2 方法 采集研究对象清晨空腹静脉血 5 mL, 以 3000 r/min, 离心半径 15 cm, 离心 10 min, 留 取上层血清,采用酶联免疫吸附法检测 BNP、 PCT、hs-CRP 水平,试剂盒均购自杭州浙大迪迅 生物基因工程有限公司,操作严格按照试剂盒说明书进行。
1.3 观察指标 (1) 比较三组血清 BNP、PCT、 hs-CRP 水平。(2)比较合并组不同心功能分级 患 者 血 清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水 平。NYHA 心 功 能分级标准:日常活动不受限制,进行一般体力活 动时不引起心悸、气喘、心绞痛等症状为Ⅰ级;体 力活动轻微受限,在休息时基本无症状,轻微体 力活动时可存在心悸、气喘、心绞痛等症状为Ⅱ 级;体力活动显著受限,休息时症状不明显,较小 体力活动时即可出现心悸、气喘、心绞痛等症状为 Ⅲ级;休息时也存在心力衰竭症状,无法从事任何 体力活动,体力活动后症状加重为Ⅳ级。(3)采 用 Pearson 相关性分析血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水 平与重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者心功能分级的相 关性。
1.4 统计学方法 采用 SPSS 23.0 统计学软件处理 数据,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,采用 t 检验,计 数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,多组间比较 采用方差分析, 采用 Pearson 相关性分析, 以 P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
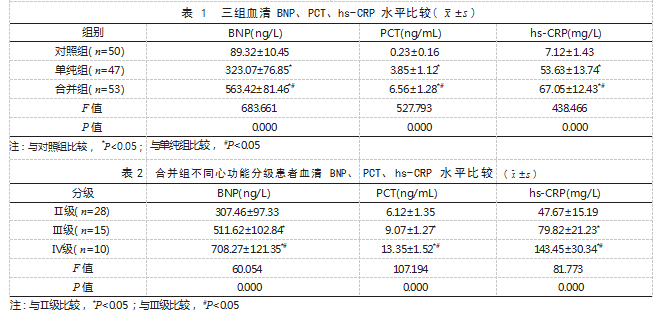
2.1 三组血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平比较 合 并组血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平均高于单纯组 和对照组,且单纯组高于对照组,差异有统计学意 义(P<0.05) 。见表 1.
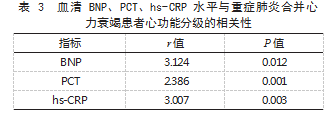
2.2 合并组不同心功能分级患者血清 BNP、PCT、 hs-CRP 水平比较 合并组心功能分级Ⅳ级患者血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平均高于Ⅱ级和Ⅲ级, 且Ⅲ级 高于Ⅱ级,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 见表 2.
2.3 血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平与重症肺炎合 并心力衰竭患者心功能分级的相关性 Pearson 相 关性分析结果显示, 血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水 平与重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者心功能分级呈正相 关( r>0. P<0.05)。见表 3.
3 讨论
重症肺炎的发病率和病死率均较高,会造成机 体多器官功能衰竭,其中心力衰竭较为多见,危及 患者生命安全 [4-5] 。因此,早期及时评估患者病情 严重程度,对改善患者预后具有重要意义。
BNP 是由心肌细胞分泌的一种血管活性物质, 当心脏负荷增加或超负荷时,其水平升高,是临床 诊断心力衰竭和评估治疗效果的重要指标 [6-7]。PCT 可反映全身炎症活跃程度,是诊断和检测炎症感染 的指标 [8-9]。hs-CRP 主要由肝脏合成,是一种全身 性炎症反应急性期的非特异性标志物,同时也是预 测心脑血管疾病的重要指标 [10-11]。
本研究结果显示, 合并组血清 BNP、PCT、hs- CRP 水平均高于对照组和单纯组,且单纯组高于 对照组; 心功能分级Ⅳ级患者血清 BNP、PCT、hs- CRP 水平均高于Ⅱ级和Ⅲ级,且Ⅲ级高于Ⅱ级; Pearson 相关性分析结果显示, 血清 BNP、PCT、hs- CRP 水平与重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者心功能分级 呈 正 相 关。 提 示 血 清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水 平 在 重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者体内呈高表达,且心功 能分级越高, 血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平越高。 分析原因为当出现心力衰竭时,患者体内血流动力 学发生改变,心脏容量负荷与心室压力变化,导致 血清 BNP 水平升高 [12] ;心力衰竭患者常存在血管 内皮功能损伤等情况,会刺激机体释放组织因子, 加重炎症反应, 导致 PCT、hs-CRP 水平升高, 且 其水平随心功能损伤程度加重而升高 [13]。
综上所述,重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者血清 BNP、PCT、hs-CRP 水平升高, 且与患者心功能分级呈正相关。
参考文献
[1] Nguyen AH, Detty SQ, Agrawal DK. Clinical Implications of High-mobility Group Box- 1 ( HMGB1 ) and the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-products ( RAGE ) in Cutaneous Malignancy: A Systematic Review[J]. Anticancer Res, 2017. 37 (1): 1-7.
[2] Guo S, Mao X, Liang M. The moderate predictive value of serial serum CRP and PCT levels for the prognosis of hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia[J]. Respir Res, 2018. 19 (1):193.
[3] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会感染学组 . 中国成人医院获得性肺炎与呼吸机相关性肺炎诊断和治疗指南(2018 年版) [J]. 中 华结核和呼吸杂志, 2018. 41 (4): 255-280.
[4] 许鹏,陈敏 . 不同 NYHA 心功能分级慢性心力衰竭患者心脏标志物四项、PCT、BNP 水平变化及临床意义 [J]. 海南医学, 2021. 32 (19): 2488-2491.
[5] 陈晓波 . 降钙素原(PCT)与 N 端钠尿肽前体(NT-proBNP)在心力衰竭诊断及预后判断的价值 [J]. 系统医学, 2021. 6 (24): 37-40.
[6] 李成理,徐亚军,张武华 . 血清 PCT 联合 IL-6、CRP 水平对重症肺炎患者病情严重程度及预后的评估价值 [J]. 实验与检 验医学, 2020. 38 (6): 1162-1165.
[7] Proboszcz M, Paplińska-Goryca M, Nejman-Gryz P, et al. A comparative study of sTREM-1. IL-6 and IL-13 concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in asthma and COPD: A preliminary study[J]. Adv Clin Exp Med, 2017. 26 (2): 231-236.
[8] Yuan S, Gao Y, Ji W, et al. The evaluation of acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II score, poisoning severity score, sequential organ failure assessment score combine with lactate to assess the prognosis of the patients with acute organophosphate pesticide poisoning[J]. Medicine ( Baltimore ), 2018. 97 (21):e10862.
[9] 芦 珊,韩英,丁栗 . 血 清 hs-CRP、cTn Ⅰ、BNP 及 PCT 联合检测对慢性心力衰竭的临床诊断价值 [J]. 热带医学杂志, 2021. 21 (2): 193-196.
[10] 尹其云,张建霞,柳贵蓉 . 高敏 C 反应蛋白、脑钠肽变化与心力衰竭患者心功能的关系 [J]. 中国当代医药, 2018. 25 (22): 66-69.
[11] 李俊梅,李荣荣,陈晓娟,等 . 血清 FSTL1、MIP-2 和 NT-proBNP 在重症肺炎合并心力衰竭患者中表达及与预后关系研 究 [J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2021. 20 (17): 1828-1831.
[12] 王敬敏,刘冬梅,徐琳,等 . 血浆 NT-proBNP 及 H-FABP 联合检测在小儿重症肺炎合并心力衰竭中的应用价值 [J]. 解放 军医药杂志, 2017. 29 (9): 106-109.
[13] 孟仙梅,林红飞,黎璞 . 心力衰竭合并重症细菌性肺炎患者BNP、CRP、PCT 的变化及其临床意义 [J]. 海南医学, 2018. 29 (24): 3417-3419.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网!
文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/yixuelunwen/63842.html