SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:观察舌下免疫治疗(SLIT) 对变应性鼻炎(AR) 患儿免疫球蛋白及 T 细胞亚群水平的影响。方法: 选取 2017 年 4 月至 2018 年 4 月该院收治的 72 例 AR 患儿进行前瞻性研究,按照随机数字表法分为研究组和对照组各 36 例。对照组采用常规治疗,研 究组在对照组基础上采用SLIT治疗。治疗2年后, 比较两组治疗前后临床症状评分、免疫球蛋白[血清尘螨特异性IgE(sIgE)、总IgE(T-IgE)、 特异性 IgG4(sIgG4)] 水平、T 细胞亚群 [CD3+、CD4+、CD8+、CD4+/CD8+] 水平和不良反应发生率。结果: 治疗后,两组喷嚏、流涕、鼻 痒及鼻塞等临床症状评分均低于治疗前,且研究组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组血清尘螨 sIgE 和 T-IgE 水平均低于治 疗前,且研究组低于对照组,两组血清尘螨 sIgG4 水平均高于治疗前,且研究组高于对照组,差异有统计学意义( P<0.05); 两组 CD3+、 CD4+ 水平和 CD4+/CD8+ 值均高于治疗前,且研究组高于对照组,两组 CD8+ 水平均低于治疗前,且研究组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义 ( P<0.05) ;两组不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。 结论: 在常规治疗基础上采用 SLIT 治疗 AR 患儿,可改善免疫球 蛋白和 T 细胞亚群水平,降低临床症状评分,效果优于单纯常规治疗。
【关键词】 变应性鼻炎,舌下免疫治疗,尘螨过敏,T 细胞亚群,免疫球蛋白,不良反应
Effects of sublingual immunotherapy on immunoglobulin and T lymphocyte subset levels in children with allergic rhinitis
AI Xue
(Department of Pediatrics of Huludao Central Hospital, Huludao 125100 Liaoning, China)
【Abstract 】 Objective: To observe effects of sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) on immunoglobulin and T lymphocyte subset levels in children with allergic rhinitis (AR). Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 72 children with AR admitted to the hospital from April 2017 to April 2018. They were divided into study group and control group according to the random number table method, 36 cases in each. The control group was treated with conventional therapy, while the study group was treated with SLIT on the basis of that of the control group. After 2 years of treatment, the clinical symptom scores, the immunoglobulin [serum dust mite specific IgE (sIgE), total IgE (T-IgE), specific IgG4 (sIgG4)] levels, the T cell subsets [CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+] levels, and incidence of adverse reactions were compared between the two groups before and after the treatment. Results: After the treatment, the scores of clinical symptoms such as sneezing, runny nose, nasal itching and nasal congestion in the two groups were lower than those before the treatment, those of the study group were lower than those of the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The levels of serum dust mite sIgE and T-IgE in the two groups were lower than those before the treatment, and those in the study group were lower than those in the control group; the levels of serum dust mite sIgG4 in the two groups were higher than those before the treatment, and that in the study group was higher than that in the control group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The levels of CD3+, CD4+ and CD4+/CD8+ in the two groups were higher than those before the treatment, and those in the study group were higher than those in the control group; the levels of CD8+ in the two groups were lower than those before the treatment, and that in the study group was lower than that in the control group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse reactions between the two groups (P>0.05). Conclusions: On the basis of the conventional treatment, SLIT can improve the levels of immunoglobulin index and the T cell subsets and reduce the clinical symptom scores in the children with AR. Moreover, it is superior to single conventional treatment.
【Keywords】 Allergic rhinitis; Sublingual immunotherapy; Mite sensitivity; T cell subset; Immunoglobulin; Adverse reaction变应性鼻炎(allergic rhinitis,AR) 是指机体 呼吸道发生变应反应,从而引发由免疫球蛋白 IgE 介导的阵发性喷嚏及鼻塞等症状,患者主要表现为 喷嚏、鼻塞、流涕等,严重时可诱发肺气肿及哮喘
等疾病 [1-2] 。已知变应原特异性免疫治疗(specific immunotherapy,SIT) 是唯一可能阻断过敏性疾病 进展的治疗方法, 包括皮下免疫治疗(subcutaneous immunotherapy,SCIT) 和舌下免疫治疗(sublingual immunotherapy, SLIT)两种常用给药方式[3-4]。其中, SLIT 是通过将自身存在的过敏原配置成不同浓度 的脱敏液,采用经口给药的方式,使患者的致敏部位与不同浓度的脱敏液进行剂量由小到大、浓度由 低到高的接触,从而使患者逐步获得对过敏原的耐 受力,具有使用方便、依从性高的优势,尤其适用 于患儿 [5] 。本文观察 SLIT 对 AR 患儿免疫球蛋白及 T 细胞亚群水平的影响。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2017 年 4 月至 2018 年 4 月 本院收治的 72 例 AR 患儿进行前瞻性研究。纳入 标准:符合儿童 AR 的诊断标准 [6] ,尘螨过敏,皮 肤点刺实验阳性为“++”及以上,血清尘螨特异 性 IgE 抗体≥2 级;变应原皮肤试验阳性;临床资 料完整。排除标准:合并严重心、肺、肾功能障碍; 合并严重精神障碍;家族遗传自身免疫性疾病或变 应性疾病;长期服用激素治疗;合并其他急、慢性 疾病;参与研究前使用 β2- 受体阻滞剂或血管紧 张素转换酶抑制剂治疗;合并其他原因导致的鼻炎; 合并哮喘。患儿家长对本研究内容了解并自愿签署 知情同意书,且研究经本院伦理委员会批准。按照 随机数字表法分为研究组和对照组各36例。研究组: 男21例,女 15例;年龄5~14岁,平均(8.46±1.26) 岁; 病程 1~4 年, 平均(2.03±0.67) 年。对照组: 男20例,女 16例;年龄5~14岁,平均(8.28±1.31) 岁; 病程 1~5 年, 平均(2.11±0.69) 年。两组一 般资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05), 有可 比性。
1.2 方法 对照组采用常规治疗。口服依巴斯汀片 (INDUSTRIAS FARMACEUTICAS ALMIRALL, S.A., 注册证号 H20140856. 10 mg), 10 mg/ 次, 1 次 /d; 盐酸左卡巴斯汀鼻喷雾剂(Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V.,国药准字 HJ20160305.10 mL ∶ 5 mg),每 次每个鼻孔各喷 2 下,2 次 /d。
研究组在对照组基础上采用 SLIT 治疗。舌下 含服粉尘螨滴剂(浙江我武生物科技股份有限公 司, 国药准字 S20060012. 粉尘螨滴剂 1 号: 蛋 白浓度 1 μg/mL;粉尘螨滴剂 2 号:蛋白浓度 10 μg/mL;粉尘螨滴剂 3 号:蛋白浓度 100 μg/mL; 粉尘螨滴剂 4 号:蛋白浓度 333 μg/mL;粉尘螨滴 剂 5 号: 蛋白浓度 1000 μg/mL), 第 1 周采用粉 尘螨滴剂 1 号治疗,第 2 周采用粉尘螨滴剂 2 号治 疗,第 3 周采用粉尘螨滴剂 3 号治疗,前 3 周的第 1~7 天的含服剂量为各自对应剂型下予以 1、2、3、 4、6、8、10 滴, 前 3 周 为初始治疗; 第 4~5 周 采用粉尘螨滴剂 4 号治疗,1 次 /d,3 滴 / 次,第6 周采用粉尘螨滴剂 5 号治疗,1 次 /d,2 滴 / 次。 滴于舌下,含 1~3 min 后吞咽,每日洗漱后早饭前 使用。两组均连续治疗 2 年。
1.3 观察指标 (1)比较两组治疗前后临床症状 评分,参照《耳鼻炎喉头颈部变态反应病学》中相 关内容对喷嚏、流涕、鼻痒及鼻塞症状进行评分 [7]。 喷嚏:1 次连续个数 <3 个计 0 分,3~9 个计 1 分, 10~14 个计 2 分, ≥ 15 个计 3 分;流涕:每日擤 鼻涕次数 ≤ 4 次计 1 分,5~9 次计 2 分, ≥ 10 次 计 3 分;鼻痒:无鼻痒感计 0 分,鼻痒间断发生计 1 分,可忍受的蚁行感计 2 分,难以忍受的蚁行感 计 3 分;鼻塞:无鼻塞症状计 0 分,呼吸时感觉到 鼻腔内阻力计 1 分,间断发生的鼻腔堵塞计 2 分, 几乎全天用口呼吸计 3 分。分值越高临床症状越严 重。(2)比较两组治疗前后免疫球蛋白水平。采 集患儿清晨空腹静脉血,离心取血清,采用酶联 免疫吸附法测定尘螨特异性 IgE(sIgE) 、总 IgE (T-IgE)、特异性 IgG4(sIgG4) 水平。(3) 比 较两组治疗前后 T 细胞亚群指标水平。采集患儿清 晨空腹静脉血,给予抗凝处理,采用流式细胞术测 定 CD3+、CD4+、CD8+ 水平, 并计算 CD4+/CD8+。(4) 比较两组不良反应发生率。
1.4 统计学方法 应用 SPSS 22.0 软件进行统计学 分析,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,采用 t 检验,计 数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,以 P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
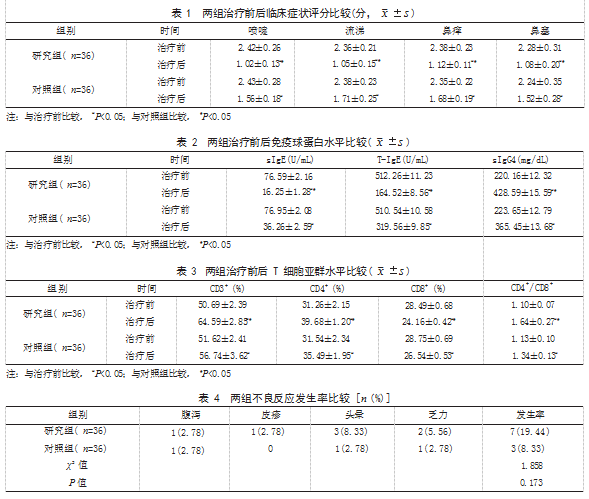
2.1 两组治疗前后临床症状评分比较 治疗前, 两组喷嚏、流涕、鼻痒及鼻塞等临床症状评分比较, 差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05); 治疗后, 两组喷 嚏、流涕、鼻痒及鼻塞等临床症状评分均明显低于 治疗前,且研究组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。见表 1.
2.2 两组治疗前后免疫球蛋白水平比较 治疗前, 两组血清尘螨 sIgE、T-IgE 和 sIgG4 水平比较, 差 异均无统计学意义(P>0.05); 治疗后, 两组血清 尘螨 sIgE 和 T-IgE 水平均明显低于治疗前,且研 究组低于对照组,两组血清尘螨 sIgG4 水平均明显 高于治疗前,且研究组高于对照组,差异有统计学 意义(P<0.05)。见表 2.
2.3 两组治疗前后 T 细胞亚群水平比较 治疗前, 两组 CD3+、CD4+、CD8+ 水平和 CD4+/CD8+ 值比较, 差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05); 治疗后, 两组CD3+、CD4+ 水平和CD4+/CD8+ 值均明显高于治疗前, 且研究组高于对照组,两组 CD8+ 水平均明显低于 治疗前,且研究组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。见表 3.
2.4 两组不良反应发生率比较 研究组不良反应 发生率为 19.44%(7/36) ,对照组不良反应发生率 为 8.33%(3/36), 两组比较, 差异无统计学意义 ( P>0.05)。见表 4.
3 讨论
AR 是由 IgE 介导的过敏性疾病,患者多表现为 鼻塞、喷嚏及流涕等症状,近年来其发病率呈明显 上升趋势 [8-9]。传统药物(如激素及抗组胺药物等) 主要是对症治疗,发挥抑制及预防变态反应发生的 作用,需要长期、反复用药,且不良反应较多。而 SLIT 是通过变应原提取物刺激机体,促进调节性 T 细胞的表达而使机体耐受同种致敏原的刺激,不仅 可以有效预防 AR 向哮喘转化,也可以有效预防新的变应原产生,且其引起的不良反应少且轻微 [10-11]; 已知 SLIT 采用舌下含服的给药方式,用药过程无痛 苦,患儿易接受,且用药场所不受限制,患儿及其 监护人不必花费大量时间前往医院 [12-13]。
本研究结果显示,研究组喷嚏、流涕、鼻痒 及鼻塞等临床症状评分均低于对照组。分析原因为 SLIT 联合常规治疗可发挥协同增效作用, 使患儿逐 步耐受致敏原,降低机体嗜酸性粒细胞中的阳离子 蛋白水平, 减弱外周淋巴细胞对变应原的增殖反应, 从而发挥脱敏作用,进而缓解临床症状 [14] 。本研 究结果同时显示,治疗后,研究组血清尘螨 sIgE、 T-IgE 水平低于对照组,sIgG4 水平高于对照组。 分析原因为在常规治疗基础上予以舌下含服粉尘螨 滴剂能促进机体产生免疫反应,降低血清尘螨 sIgE 和 T-IgE 水平,有效抑制过敏原复合物,从而抑制 过敏原引起的特异性反应。已知 AR 致敏过程存在 明显的 T 细胞数量及免疫功能失衡现象,故对 T 细胞进行监测可避免出现不必要的不良反应 [15] 。
本研究结果还显示,研究组 CD3+、CD4+ 水平和 CD4+/ CD8+ 值均高于对照组,CD8+ 水平低于对照组。分 析原因可能与 SCIT 可纠正免疫失衡状态有关。本研究结果又显示,两组不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义。提示采用SLIT治疗未增加安全风险。 因本研究纳入的样本量较少,其结果尚需后期加大 样本量开展深入研究予以印证。
综上所述,在常规治疗基础上采用 SLIT 治疗AR 患儿, 可改善免疫球蛋白和 T 细胞亚群水平, 降低临床症状评分,效果优于单纯常规治疗。
参考文献
[1] 董博,金修桥 . 变应性鼻炎治疗的研究进展 [J]. 医学综述,2021.27(1):141-145.
[2] 董春花,马新春,张英 . 变应性鼻炎患者血清 OPN、NF- κB与 sIgE 水平的相关性 [J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2021. 42(4):473-475.
[3] Klimek L,Sperl A,Becker S, et al. Current therapeuticalstrategies for allergic rhinitis[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother,2019.20(1):83-89.
[4] Licari A, Castagnoli R, De Filippo M, et al. Current and emergingbiologic therapies for allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis[J].Expert Opin Biol Ther,2020.20(6):609-619.
[5] Liu ZF,Lu HY,Feng X, et al. Predictive methods for efficacyof house dust mite subcutaneous immunotherapy in allergic rhinitispatients:a prospective study in a Chinese population[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol,2020.10(3):314-319.
[6] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组,中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组、小儿学组,中华儿科杂 志编辑委员会 . 儿童变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2010 年,重庆) [J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2011. 46(1) :7-8.
[7]顾之燕,李源 . 耳鼻炎喉头颈部变态反应病学 [M]. 北京:人 民卫生出版社,2012:126-128.
[8] 缪建良,陈云华,郭建林,等 . 舌下免疫治疗变应性鼻炎的 疗效分析 [J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2021. 29(2):106-108.
[9]刘振春 . 粉尘螨滴剂舌下含服特异性免疫治疗小儿过敏性哮 喘效果观察 [J]. 中国保健营养,2020.30(22):101.
[10] 李金玲,赵长青,李璐鑫 . 舌下免疫治疗单一和多重致敏变 应性鼻炎疗效及依从性分析 [J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2020.28(4):255-258.
[11] 李付广,王芳,杨桂枝,等 . 儿童过敏性哮喘特异性免疫治疗过程中 IL-10、TGF- β1 和 CD4+CD25+T 细胞的变化 [J]. 现 代免疫学,2009.29(1):59-63.Brüggenjürgen B,
[12] Reinhold T. Cost-effectiveness of grass pollen subcutaneous immunotherapy(SCIT)compared to sublingual immunotherapy(SCIT)and symptomatic treatment in Austria, Spain,and Switzerland[J]. J Med Econ,2018.21(4):374-381.
[13] Liu W,Zeng Q,He C, et al. Compliance,efficacy,and safety of subcutaneous and sublingual immunotherapy in children with allergic rhinitis[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol,2021.32(1):86-91.
[14] Molero-Abraham M,Sanchez-Trincado JL,Gomez-Perosanz M,et al Human oral epithelial cells impair bacteria-mediated
maturation of dendritic cells and render t cells unresponsive to stimulation[J]. Front Immunol,2019(10):1434.
[15] Li J,Raghav P,Hu C. Ajwain oil attenuates allergic response of ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis via alteration of inflammatory,oxidative stress,and Th1/Th2 responses[J]. J Food Biochem. 2021.45(12):13963.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网!
文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/yixuelunwen/57102.html