SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:探讨血清白蛋白(ALB) 、胆碱酯酶(CHE) 、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)和 γ- 谷氨酰转肽酶(γ-GT)水平检 测在肝硬化诊断中的应用价值。方法: 选取 2019 年 1 月至 2021 年 6 月本院收治的 75 例肝硬化患者为肝硬化组。选取同期于本院体检的 75 名健康人作为对照组, 两组均行血清 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水平检测。比较两组血清 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水平, 比较肝硬化 组不同肝功能分级患者血清 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水平, 采用 Spearman 相关性分析, 探讨血清 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水平与肝硬 化患者肝功能的相关性。 结果: 肝硬化组血清 ALB、CHE 水平低于对照组, ALT、γ-GT 水平高于对照组, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 75 例肝硬化患者中,Child-Pugh 分级为 A 级 24 例,B 级 32 例,C 级 19 例。C 级肝硬化患者 ALB、CHE 水平均低于 B 级和 A 级患者, 且 B 级低于 A 级; C 级肝硬化患者 ALT、γ-GT 水平均高于 B 级和 A 级患者, 且 B 级高于 A 级, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05) 。Spearman 相关性分析结果显示,血清 ALB、CHE 水平与肝硬化患者肝功能 Child-Pugh 分级呈负相关( r<0. P<0.05) ; 血清 ALT、γ-GT 水平与 肝硬化患者肝功能 Child-Pugh 分级呈正相关( r>0. P<0.05)。 结论: 血清 ALB、CHE、γ-GT、ALT 水平用于肝硬化诊断具有临床价值, 可反映肝硬化患者肝功能。
【关键词】白蛋白,胆碱酯酶,γ- 谷氨酰转肽酶,丙氨酸氨基转移酶,肝硬化,诊断,肝功能分级
Application value of serum ALB, CHE, γ-GT and ALT in diagnosis of liver cirrhosis
HU Xiaoju
(Department of Clinical Laboratory of Ye County People’s Hospital, Pingdingshan 47200 Henan, China)
【 Abstract 】 Objective: To investigate application value of serum albumin (ALB), cholinesterase (CHE), alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GT) in diagnosis of liver cirrhosis. Methods: 75 patients with liver cirrhosis admitted to this hospital from January 2019 to June 2021 were selected as cirrhosis group, and 75 healthy people who underwent physical examination during the same period were selected as control group. The serum ALB, ALT, CHE and γ-GT levels were detected in both groups. The levels of serum ALB, ALT, CHE and γ-GT were compared between the two groups. The levels of serum ALB, ALT, CHE and γ-GT in the patients with different liver function classifications in the cirrhosis group were compared. Spearman correlation analysis was used to investigate the correlations among the serum ALB, ALT, CHE, γ-GT levels and the liver function in the patients with liver cirrhosis. Results: The levels of serum ALB and CHE in the liver cirrhosis group were lower than those in the control group, the levels of ALT and γ-GT were higher than those in control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Among the 75 patients with liver cirrhosis, 24 cases had Child-Pugh classification A, 32 cases had the classification B, and 9 cases had the classification C. The levels of ALB and CHE in the patients with Child-Pugh classification C were lower than those in the patients with classification B and classification A, and those in the patients with classification B were lower than those in the patients with classification A; the levels of ALT and γ-GT in the patients with Child-Pugh classification C cirrhosis were higher than those in the patients with classification B and classification A, and those in the patients with classification B higher lower than those in the patients with classification A; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Spearman correlation analysis showed that the serum ALB and CHE levels were negatively correlated with the Child-Pugh classification of liver function in the patients with liver cirrhosis (r<0. P<0.05), while the serum ALT and γ-GT levels were positively correlated with the Child-Pugh classification (r>0. P<0.05). Conclusions: The serum ALB, CHE, γ-GT and ALT levels have clinical value in the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis, which can reflect the liver function of the patients with liver cirrhosis.
【Keywords】 Albumin; Cholinesterase; γ-glutamyl transpeptidase; Alanine aminotransferase; Liver cirrhosis; Diagnosis; Liver function classification
肝硬化可进展至肝癌,威胁患者生命安全 [1-2]。 病理组织活检是诊断肝硬化的金标准,但操作难度高、成本高、创伤大,难以作为常用筛查方法 [3]。 本文探讨血清白蛋白(ALB) 、胆碱酯酶(CHE) 、 丙 氨酸 氨基 转 移酶(ALT) 和 γ- 谷 氨 酰转 肽酶 (γ -GT)水平检测在肝硬化诊断中的应用价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2019 年 1 月至 2021 年 6 月本院收治的 75 例肝硬化患者进行前瞻性研究,作为 肝硬化组。纳入标准:符合肝硬化标准 [4] 。排除标 准:合并精神障碍、认知异常;有不良饮酒史、药 物性肝脏损伤;既往接受食管静脉曲张套扎术治疗; 妊娠期或哺乳期女性;参与研究前服用影响血清学 指标的药物。选取同期于本院体检的 75 名健康人 作为对照组。肝硬化组:男 41 例,女 34 例;年龄 30~72 岁, 平均(56.28±5.69)岁。对照组:男 40 名, 女 35 名; 年龄 30~73 岁, 平均(57.15±5.72) 岁。 两组性别、年龄等一般资料比较,差异无统计学意 义(P>0.05),有可比性。
1.2 方法 肝硬化组在入院第 2 天、体检者在体 检当天, 于 8:00 - 9:00 采集空腹静脉血 4 mL, 分 离血清,采用立 7080 型全自动生化分析仪(酶 联 免 疫 法) 检 测 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水 平, 试剂盒由贝尔曼库尔特公司生产。ALT 正常参考值: 0~40 U/L;ALB 正常参考值:35~55 g/L;CHE 正常 参考值:3700~13 200 U/L;γ-GT 正常参考值:男 性 11~50 U/L,女性 7~32 U/L。
1.3 观 察 指 标 (1) 比 较 两 组 血 清 ALB、ALT、 CHE、γ-GT 水平。(2) 比较肝硬化组不同功 能 分 级 患 者 血 清 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水 平。 (3) 采用 Spearman 相关性分析, 探讨血清 ALB、 ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水平与肝硬化患者肝功能分级 的相关性。
1.4 统计学方法 应用 SPSS 20.0 软件进行统计学 分析,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,两组间比较采 用 t 检验,多组间比较采用方差分析,计数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,相关性分析采用 Spearman 相关性分析, 以 P<0.05 为差异有统计学 意义。
2 结果
2.1 两 组 血 清 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水 平 比 较 肝硬化组血清 ALB、CHE 水平均低于对照组, ALT、γ-GT 水平均高于对照组,差异均有统计学 意义(P<0.05)。见表 1.
2.2 肝硬化组不同肝功能分级患者血清 ALB、 ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水平比较 75 例肝硬化患者中, Child-Pugh 分级为 A 级 24 例,B 级 32 例,C 级 19 例。Child-Pugh 分 级 C 级 肝 硬 化 患 者 ALB、CHE 水平均低于 B 级和 A 级患者,且 B 级低于 A 级; Child-Pugh 分级 C 级肝硬化患者 ALT、γ-GT 水平 均高于 B 级和 A 级患者,且 B 级高于 A 级,差异 均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 2.
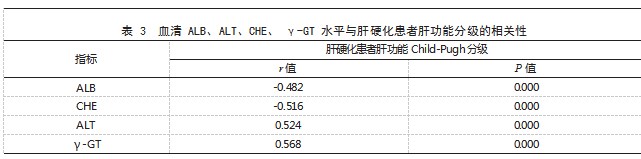
2.3 血清 ALB、ALT、CHE、γ-GT 水平与肝硬化 患者肝功能分级的相关性 Spearman 相关性分析结 果显示,血清 ALB、CHE 水平与肝硬化患者肝功 能 Child-Pugh 分 级 呈 负 相关( r<0. P<0.05); 血 清 ALT、γ-GT 水 平 与 肝 硬 化 患 者 肝 功 能 Child- Pugh 分级呈正相关( r>0. P<0.05)。见表 3.
3 讨论
肝硬化是临床常见肝病类型,多由病毒性肝炎 导致,其病情发展复杂、病程长,预后差 [5] 。提高 肝硬化早期诊断率,及时遏制疾病进展,对改善患 者预后具有积极意义 [6-8]。
ALB、ALT 是评价肝脏急性损伤程度的敏感指标, ALB 是由肝脏合成的特异性蛋白, 可有效评 价肝脏蛋白质合成及储备功能, ALT 主要分布在肝 细胞胞浆内,是评价肝功能的重要指标 [9] 。CHE 是 由肝细胞合成的水解催化酶,可用于评价肝细胞 合成、肝脏储备功能 [10]。γ-GT 来源于肝脏组织, 由肝细胞线粒体产生,主要局限分布在肝细胞质内 与肝内胆管上皮中,从胆道排泄,可反映肝细胞损 害程度 [11] 。本研究结果显示, 肝硬化组血清 ALB、 CHE 水平低于对照组,ALT、γ-GT 水平高于对照 组。分析原因为肝硬化患者肝细胞与肝脏线粒体损 害,肝脏储备功能降低,致 ALB 水平降低 [12] 。随 着肝细胞损害及细胞损伤程度加重,细胞质内 ALT 因长期释放而出现衰竭情况,相反血清 ALT 水平 升高 [13]。CHE 由肝细胞合成,当肝脏受损,肝细 胞损害, 肝脏合成、代谢功能异常, CHE 合成量及 释放量减少,故使血清 CHE 水平降低。γ-GT 在 肝细胞质内有较高含量,正常血清 γ-GT 呈低浓 度表达,若肝细胞合成、分泌功能受损,胆管内压 增加,会相应增强肝脏合成,减少胆道排泄量,使 血清 γ-GT 含量升高;同时肝细胞及周围组织受 炎症刺激,加重肝细胞破坏程度,使肝细胞膜通透 性增加,导致血清中 γ-GT 含量升高 [14-16]。
本研究结果同时显示,Child-Pugh 分级 C 级肝 硬化患者 ALB、CHE 水平均低于 B 级和 A 级患者, 且 B 级低 于 A 级;Child-Pugh 分 级 C 级肝 硬化 患 者 ALT、γ-GT 水平均高于 B 级和 A 级患者, 且 B 级高于 A 级;Spearman 相关性分析结果显示,血 清 ALB、CHE 水平与肝硬化患者肝功能 Child-Pugh 分级呈负相关( r<0. P<0.05), 血清 ALT、γ-GT 水平与肝硬化患者肝功能 Child-Pugh 分级呈正相 关( r>0. P<0.05) 。提示血清 ALB、CHE、γ-GT、 ALT 水平用于临床诊断肝硬化可有效评估患者病情 进展。
综上所述, 血清 ALB、CHE、γ-GT、ALT 水 平用于肝硬化诊断具有临床价值,可反映肝硬化患者肝功能。
参考文献
[1] 李正鑫,陈洋溢,赵志敏,等 . 基于肝脏病理学对慢性乙型肝炎肝硬化患者 FibroTouch 测量值的影响因素分析 [J]. 临床 肝胆病杂志,2019.35(2):107-113.
[2] 胡丽,张雅丽,谭红阳,等 . 肝炎后肝硬化病人症状群纵向研究进展 [J]. 护理研究,2019.33(6):85-90.
[3] 曹竹君,王晖 . 细胞死亡标志物角蛋白 18 片段与乙型肝炎肝硬化疾病进展和预后的关系 [J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2019. 35(9):2061.
[4] 王蔚文 . 临床疾病诊断与疗效判断标准 [M]. 北京:科学技术文献出版社,2010:226.
[5] 张静雯,时永全,韩英 . 肝硬化的治疗进展 [J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2015.31(3):465-468.
[6] 刘斌, 方正亚, 孟冬梅 . 肝硬化并发症治疗及预防研究进展 [J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016.30(12):1152-1155.
[7] 王海峰 . 血清生化指标水平对肝炎肝硬化患者肝功能的评估价值 [J]. 医疗装备,2020.33(12):48-49.
[8] 钱香蓓 . 两种全自动生化分析仪测定血清肝功能指标的比较 [J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊) , 2016. 16(81):113-114.
[9] 马丽君, 何聪 . APRI 及 S 指数与乙型肝炎肝硬化 Child-Pugh肝功能分级的关系 [J]. 肝脏,2019.24(4):114-115.
[10] 张映华, 古晓娟 . CHE,ALB, CHO 在肝炎肝硬化患者中的表达及诊断效能影响研究 [J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2020. 27(3):497-501.
[11] 任书勤, 章阳 . 肝癌患者血清 γ-GT,GLB,ALB,CHOL 及AFP 水平变化及其临床意义 [J]. 标记免疫分析与临床, 2020. 27(3):398-404.
[12] 吕日英, 李仕雄, 向文耀 . FibroTouch 联合 ALB,ALP,AFU对肝硬化的诊断价值及预后评价 [J]. 现代医学, 2020. 48(4):64-67.
[13] 桂红莲,谢青 . ALT 正常的慢性 HBV 感染者的抗病毒治疗时机选择 [J]. 中华肝脏病杂志,2020.28(12):988-991.
[14] 李丹丹,杜燕娥,段亮,等 . 肝硬化相关血清学指标与Child-Pugh 分级的关系 [J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2019. 44(3):336-339.
[15] 徐惠敏,兰小勤,纪雅丽 . 肝功能衰竭合并肝硬化患者血清 γ- 谷氨酰转肽酶与前白蛋白水平的相关性 [J]. 中国肝脏病 杂志(电子版),2018.10(3):90-93.
[16] 吴芳,孙凤霞,徐春军 . γ- 谷氨酰转肽酶在肝脏疾病诊断和预后中的意义 [J]. 中华实验和临床感染病杂志(电子版), 2015.9(5):616-620.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网! 文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/yixuelunwen/51998.html