SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:探讨尿干化学亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测在尿路细菌感染诊断中的效能。方法: 选取 2019 年 6 月至 2021 年 6 月该院 收治的 200 例疑似尿路感染患者进行前瞻性研究,以尿培养结果为金标准,统计尿干化学亚硝酸盐、白细胞单项及联合检测结果,并比较 尿干化学亚硝酸盐、白细胞单项及联合检测在尿路感染诊断中的效能。 结果: 200 份尿培养共 78 份阳性,阳性率为 39.00%;其中大肠埃 希菌占比最高为 38.46%,其次是铜绿假单胞菌为 12.82%,粪肠球菌为 11.54%,其余细菌均在 10% 以下; 200 份尿液标本中 31 份亚硝酸 盐阳性, 35 份白细胞阳性, 106 份亚硝酸盐联合白细胞阳性;亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测诊断尿路感染的灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值均高 于单项检测,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05) ;亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测诊断尿路感染的阴性预测值高于白细胞单项检测,差异有统计学意 义(P<0.05) ;亚硝酸盐检测诊断尿路感染的特异度和阳性预测值均高于白细胞检测,差异有统计学意义( P<0.05) ;亚硝酸盐与白细胞 单项检测诊断尿路感染的灵敏度和阴性预测值比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论: 尿干化学亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测在尿路感 染诊断中的效能高于两者单项检测。
Efficacy of urine dry chemical nitrite combined with white blood cell detection in diagnosis of urinary tract bacterial infection
WU Bing
(Department of Clinical Laboratory of Jinqiu Hospital, Shenyang 110016 Liaoning, China)
【 Abstract 】 Objective: To investigate efficacy of urine dry chemical nitrite combined with white blood cell detection in diagnosis of urinary tract bacterial infection. Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 200 patients with suspected urinary tract infection in the hospital from June 2019 to June 2021. Using the results of urine culture as the gold standard, the results of single and combined detection of urine dry chemistry nitrite and white blood cells were statistically analyzed. The efficacies of single and combined detection of urine dry chemistry nitrite and white blood cells in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection were compared. Results: A total of 78 of 200 urine cultures were positive with a positive rate of 39.00%. Among them, Escherichia coli accounted for 38.46%, followed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa of 12.82%, Enterococcus faecalis of 11.54%, and the rest of the bacteria were below 10%. Among the 200 urine samples, 31 were positive for nitrite, 35 were positive for white blood cells, and 106 were positive for nitrite combined with white blood cells. The sensitivity, the specificity and positive predictive value of nitrite combined with white blood cell detection in the diagnosis of the urinary tract infection were higher than those of single detection, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The negative predictive value of nitrite combined with white blood cell detection in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection was higher than that of single white blood cell detection, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The specificity and the positive predictive value of nitrite detection in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection were higher than those of white blood cell detection, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). However, there were no significant differences in the sensitivity and the negative predictive value between single nitrite detection and single white blood cell detection in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection (P>0.05). Conclusions: The efficacy of urine dry chemical nitrite combined with white blood cell detection in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection is higher than that of single detection.
【Keywords】 Urinary dry chemistry; Nitrite; White blood cell; Detection; Diagnosis; Urinary tract infection; Efficacy
尿路感染是泌尿外科较为常见的疾病,是由于 病原微生物入侵尿道引发,主要临床表现为尿痛、 尿频、尿道灼烧感等, 甚至出现腰痛、血尿等症状, 严重影响患者生命质量 [1]。尿培养是诊断尿路感染 的首选方法,但技术要求和检测成本均较高,且检测所需时间较长 [2] 。亚硝酸盐、白细胞是临床诊断 尿路感染的重要指标,尿干化学分析法与全自动尿 沉渣定量分析可快速识别亚硝酸盐、白细胞,并进 行定量分析,操作简单、准确率高,在临床医学中 广泛应用 [3-4] 。本文探讨尿干化学亚硝酸盐联合白 细胞检测在尿路细菌感染诊断中的效能。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2019 年 6 月至 2021 年 6 月于本院就诊的 200 例疑似尿路感染患者进行前瞻性研 究。纳入标准:存在尿频、膀胱不适、会阴部不适 等症状;理解、表达、认知能力正常;临床资料齐全。 排除标准:合并精神类疾病,意识不清;合并其他 泌尿系统疾病; 肝、肾等脏器功能障碍。其中男 92 例,女 108例;年龄 23~59 岁, 平均(38.57±5.32 ) 岁;体质量指数 19.21~25.97 kg/m2 ,平均( 23.49± 1.62 ) kg/m2.
1.2 方法 全部患者均常规清洗外阴、尿道口, 在无菌条件下收集尿液,取 10 mL 中段晨尿在 2 h 内送检。
尿培养:将收集的尿液标本摇晃均匀, 使用 1 μL 一次性定量接种环,将 1 环尿液均匀涂抹在 血琼脂平板上接种,培养箱温度设置为 37 ℃, 将 其置于培养箱培养 18~24 h,应用 VITEK-AMS 60 型全自动细菌鉴定仪观察并记录菌落数。
尿干化学亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测:将收集的 尿液标本摇晃均匀,使用尿液化学分析仪(桂林市 华通医用仪器有限公司,桂械注准 20172400041. 型 号: HT-2000A)检测尿常规亚硝酸盐,使用 尿沉渣分析系统(烟台开发区宝威生物技术有限 公司,鲁械注准 20142220164 ,型号规格: BW- 1000)进行白细胞计数。
1.3 观察指标 ( 1 )尿培养结果。以《全国临床 检验操作规程》为依据,尿培养阳性标准:尿液中 段培养结果为革兰阳性球菌菌数超过 104 CFU/mL, 或革兰阴性杆菌菌数超过 105 CFU/mL ;并统计病原 菌类型及菌株数量。(2)尿干化学亚硝酸盐、白 细胞单项及联合检测结果。以《全国临床检验操 作规程》为依据,亚硝酸盐阳性标准:尿干化学中 亚硝酸盐检测结果阳性;白细胞阳性标准:白细 胞 >30 个 /mL。( 3)以尿培养结果作为金标准, 比较尿干化学亚硝酸盐、白细胞单项及联合检测在 尿路感染诊断中的效能,包括灵敏度、特异性、阳 性预测值、阴性预测值。
1.4 统计学方法 应用 SPSS 22.0 软件进行统计学 分析,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,采用 t 检验,计 数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,以 P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
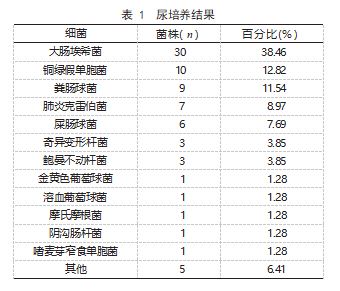
2.1 尿 培 养 结 果 200 份 尿培养 共 78 份 阳性, 阳性率为 39.00% ;其中大肠埃希菌占比最高为 38.46%, 其次是铜绿假单胞菌为 12.82%, 粪肠球 菌为 11.54%,其余细菌均在 10% 以下。见表 1.
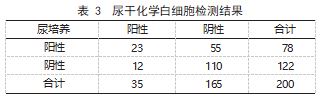
2.2 尿干化学亚硝酸盐、白细胞单项及联合检测 结果 200 份尿液标本中 31 份亚硝酸盐阳性, 35 份白细胞阳性, 106 份亚硝酸盐、白细胞联合检测 阳性。见表 2、3、4.
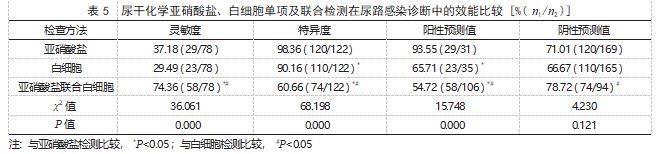
2.3 尿干化学亚硝酸盐、白细胞单项及联合检测 在尿路感染诊断中的效能比较 亚硝酸盐联合白 细胞检测诊断尿路感染的灵敏度、特异度、阳性 预测值均高于二者单项检测,差异有统计学意义 ( P<0.05 ) ;亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测诊断尿路感 染的阴性预测值高于白细胞检测,差异有统计学意 义(P<0.05) ;亚硝酸盐检测诊断尿路感染的特异 度和阳性预测值均高于白细胞检测,差异有统计学 意义(P<0.05) ;亚硝酸盐与白细胞检测单项检测 诊断尿路感染的灵敏度和阴性预测值比较,差异均 无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表 5.
3 讨论
尿路感染发病率较高,多发于老年群体、育龄 期女性、免疫力低下者,典型症状为膀胱刺激症 [5-6]。 若未及时治疗,可进一步发展为慢性膀胱炎、肾乳 头坏死、肾盂肾炎等,危害患者生命健康 [7-8] 。以 往常采用尿培养诊断, 但用时较长, 检测费用较高, 易延误病情,增加患者经济负担 [9-10] 。尿干化学分 析法为一种新颖检测方法,通过分析尿液中的亚硝 酸盐、白细胞等成分,可有效避免其他成分对结果 的干扰,较为准确、高效 [11-12]。
本研究结果显示, 200 份尿培养共 78 份阳性, 阳性率为 39.00%, 其中 31 份亚硝酸盐阳性, 35 份 白细胞阳性, 106 份亚硝酸盐、白细胞联合检测阳 性;亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测诊断尿路感染的灵敏 度、特异度、阳性预测值均高于单项检测。提示 尿干化学中亚硝酸盐、白细胞检测是诊断排除尿 路感染的重要方法,且二者联合检测对筛查、识别 尿路感染具有重要意义。分析原因可能与正常尿液 中存在硝酸盐,尿路感染时可将其还原为亚硝酸盐 有关 [13] 。但亚硝酸盐阳性需满足病原菌、尿液停 留时间等多种条件,致使亚硝酸盐检测的灵敏度较 低 [14] 。白细胞检测诊断尿路感染具有方便快捷的 优点,能够较大范围进行筛查,但由于混入鳞状上 皮细胞的酯酶会造成假阳性,在临床诊断中存在较 高的误诊率 [15] 。故尿液标本采用亚硝酸盐联合白 细胞检测可取长补短,对尿常规指标进行精准检 测,并定量分析数据,可提高诊断的准确率,以便 患者及时进行治疗,现已成为临床筛查尿路感染的 重要方法。
综上所述,尿干化学亚硝酸盐联合白细胞检测 在尿路感染诊断中的效能高于两者单项检测。
参考文献
[1] de Cueto M, Aliaga L, Alós JI, et al. Executive summary of the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract infection: Guidelines of the Spanish Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases ( SEIMC ) [J]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol clin, 2017. 35 ( 5 ):314-320.
[2] 熊敏,罗建宏,孙学娇,等 . 规范尿培养标本留取流程对标本污染率的影响 [J]. 现代医药卫生, 2021. 37 ( 20 ): 3523-3526.
[3] 瞿易,唐友东 . 尿白细胞、细菌及亚硝酸盐联合检测在尿路感染诊断中的应用价值 [J]. 包头医学院学报, 2018. 34 ( 1 ):73-74.
[4] 覃培栩,徐少林,潘良秋,等 . 尿干化学亚硝酸盐和白细胞试验对临床尿路感染的诊断价值 [J]. 医药前沿, 2015 ( 20 ):380-381.
[5] Jayakumar I, Mathaiyan J, Mandal J, et al. Impact of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring on Once-Daily Regimen of Amikacin in Patients With Urinary Tract Infection: A Prospective Observational Study[J]. Ther Drug Monit, 2020. 42 ( 6 ): 841-847.
[6] 纪凤卿,刘伟民,陈君颖,等 . UN2000 尿液全自动化流水线系统和中段尿培养检测在尿路感染诊断中的应用 [J]. 检验医 学与临床, 2021. 18 ( 23 ): 3468-3471.
[7] 梅方超,戴海英,尚小玲,等 . 尿液 HBP、 LE、U-NIT 和 WBC 联合检测与尿液细菌定量培养对急性尿道感染的诊断意 义 [J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2018. 33 ( 5 ): 126-128.
[8] 杜颖, 冯景, 杨传信, 等 . 尿常规及尿液定量分析参数在早期尿路感染经验性用药中的应用 [J]. 检验医学, 2020. 35 ( 10 ): 1046-1048.
[9] 李佳林,包野春,王会中 . 尿常规亚硝酸盐、白细胞酯酶检测及细菌计数对尿路感染的诊断价值 [J]. 检验医学与临床, 2017. 14 ( 1 ): 54-55.
[10] 路琳君,孙梦甜,刘春晖,等 . 联合应用尿液干化学法与尿沉渣镜检法进行白细胞检验的临床价值探讨 [J]. 中国卫生检 验杂志, 2019. 29 ( 7 ): 860-861.
[11] 陈梅英,傅春花,郑小霞 . 尿干化学白细胞及亚硝酸盐和沉渣细菌在尿路感染筛查中的临床意义 [J]. 基层医学论坛, 2016. 20 ( 7 ): 938-939.
[12] 周晓娟 . 尿白细胞、细菌定量联合白细胞酯酶和亚硝酸盐定性试验对尿路感染的诊断价值 [J]. 浙江医学教育, 2013. 12 ( 4 ): 61-63.
[13] 蔡斌 . 尿白细胞酯酶、亚硝酸盐和血 C 反应蛋白在细菌性尿路感染筛查中的临床价值 [J]. 智慧健康, 2021. 7 ( 1 ): 6-8.
[14] 韩洋 . 尿路结石并发感染患者尿液亚硝酸盐与白细胞检测分析 [J]. 当代医学, 2021. 27 ( 8 ): 175-176.
[15] 周晓君 . 尿白细胞、细菌及亚硝酸盐联合检测在尿路感染诊断中的应用分析 [J]. 临床检验杂志(电子版), 2020. 9 ( 3 ):272-273.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网!
文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/yixuelunwen/63763.html