SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:比较不同中医证型 2 型糖尿病(T2DM)患者血脂、血糖和 C 反应蛋白(CRP)水平。方法: 选取 2019 年 6 月至 2022 年 6 月该院收治的 300 例T2DM 患者进行前瞻性研究, 观察其不同中医证型分布, 依据不同中医证型将其分为湿热困脾证组( n=117)、 阴虚热盛证组( n=63) 、气阴两虚证组( n=45) 、血瘀脉络证组( n=42) 、阴阳两虚证组( n=33) ,测定并比较各组血脂指标组 [ 总胆固 醇(TC) 、三酰甘油(TG) ] 水平、血糖指标 [ 空腹血糖(FPG) 、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c) ] 水平和 C 反应蛋白(CRP) 水平。 结果: 300 例 T2DM 患者中,湿热困脾证占比为 39.00%,阴虚热盛证占比为 21.00%,气阴两虚证占比为 15.00%,血瘀脉络证占比为 14.00%,阴阳 两虚证占比为 11.00%。湿热困脾证组 TC、TG 水平高于阴虚热盛证组、气阴两虚证组、血瘀脉络证组和阴阳两虚证组;阴阳两虚证组 TC 水平低于血瘀脉络证组;阴阳两虚证组 TG 水平低于阴虚热盛证组和气阴两虚证组,差异均有统计学意义( P<0.05)。阴虚热盛证组 FPG 和 HbA1c 水平高于湿热困脾证组、气阴两虚证组、血瘀脉络证组和阴阳两虚证组;湿热困脾证组 HbA1c 水平低于气阴两虚证组、血瘀脉 络证组和阴阳两虚证组, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05) 。阴阳两虚证组 CRP 水平高于湿热困脾证组、阴虚热盛证组、气阴两虚证组和血 瘀脉络证组;湿热困脾证组 CRP 水平高于阴虚热盛证组、气阴两虚证组和血瘀脉络证组;血瘀脉络证组 CRP 水平高于阴虚热盛证组、气 阴两虚证组;气阴两虚证组 CRP水平高于阴虚热盛证组, 差异均有统计学意义( P<0.05)。结论:T2DM 患者的中医证型以湿热困脾证为主, 其 TC、TG 水平较高,T2DM 阴虚热盛证患者 FPG、HbA1c 水平较高,T2DM 阴阳两虚证患者 CRP 水平较高。
Comparison of blood lipids, blood glucose and C-reactive protein levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with different TCM syndrome types
XIA Chunxiao
(Suburban Friendship Office Community Health Service Center of the Central Hospital of Jiamusi City,
Jiamusi 154002 Heilongjiang, China)
【Abstract 】Objective: To compare blood lipids, blood glucose and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients (T2DM) with different TCM syndrome types. Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 300 patients with T2DM admitted to the hospital from June 2019 to June 2022. The distribution of different TCM syndromes was observed. According to different TCM syndromes, they were divided into dampness- heat stagnating spleen syndrome (n= 117), yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome group (n= 63), qi and yin deficiency syndrome group (n= 45), blood stasis syndrome group (n= 42), and yin and yang deficiency syndrome group (n= 33). The levels ofblood lipid indexes [total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG)], blood glucose indexes [fasting blood glucose (FPG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c)] and C-reactive protein (CRP) were measured and compared among these groups. Results: Among the 300 patients with T2DM, the proportion of dampness-heat stagnating spleen syndrome was 39.00%, the proportion of yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome was 21.00%, the proportion of qi and yin deficiency syndrome was 15.00%, the proportion of blood stasis syndrome was 14.00%, and the proportion of yin and yang deficiency syndrome was 11.00%. The levels of TC and TG in the dampness-heat stagnating spleen syndrome group were higher than those in the yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome group, the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group, the blood stasis syndrome group and the yin and yang deficiency syndrome group; the TC level of yin and yang deficiency syndrome group was lower than that of blood stasis syndrome group; the TG level in the yin and yang deficiency syndrome group was lower than that in the yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome group and the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The levels of FPG and HbA1c in the yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome group were higher than those in the d dampness-heat stagnating spleen syndrome group, the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group, the blood stasis syndrome group and the yin and yang deficiency syndrome group; the level of HbA1c in the dampness-heat stagnating spleen syndrome group was lower than that in the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group, the blood stasis syndrome group and the yin and yang deficiency syndrome group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The level of CRP in the Yin and Yang deficiency syndrome group was higher than that in the dampness- heat stagnating spleen syndrome group, the yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome group, the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group and the blood stasis syndrome group; the CRP level in the dampness-heat stagnating spleen syndrome group was higher than that in the yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome
group, the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group and the blood stasis syndrome group; the level of CRP in the blood stasis syndrome group was higher than that in the yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome group and the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group; the CRP level in the qi and yin deficiency syndrome group was higher than that in the yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusions: The TCM syndromes of the T2DM patients are mainly dampness-heat stagnating spleen syndrome, and their TC and TG levels are higher. Further, the FPG and HbA1 c levels are higher in the T2DM patients with yin deficiency and heat excess syndrome, and the CRP levels are higher in the T2DM patients with yin and yang deficiency syndrome.
【Keywords】 Diabetes; TCM syndrome type; Blood glucose; Blood lipid; C-reactive protein
中医学将 2 型糖尿病(T2DM) 归属于“消渴” 范畴, 阴虚为本、燥热为标是其基本病机, 肺、脾、 肾为主要病变脏腑,三脏互相影响,消渴日久耗伤 气阴,阴损及阳,阴阳俱虚,血脉疲滞 [1-2] 。探究 消渴病不同中医证型患者的血脂、血糖指标水平特 点,可为临床治疗提供参考,提高消渴病治疗效 果 [3] 。本文比较不同中医证型 T2DM 患者的血脂、 血糖和 C 反应蛋白(CRP)水平。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2019 年 6 月至 2022 年 6 月 本院收治的 300 例 T2DM 患者进行前瞻性研究。纳 入标准:符合中西医 T2DM 诊断标准 [4-5] 。排除标 准:继发性糖尿病;合并精神疾病;合并传染性 疾病;合并恶性肿瘤;严重肝、肾功能不全。患 者及家属对本研究内容了解且自愿签署知情同意 书,研究经本院伦理委员会审批通过(伦理批号: 2019006001A)。患者中男 183 例, 女 117 例; 年 龄 34~76 岁,平均(57.91±3.68)岁。
1.2 方法 依据不同中医证型将其分为湿热困脾 证组(117 例)、阴虚热盛证组(63 例) 、气阴两 虚证组(45 例) 、血瘀脉络证组(42 例) 、阴阳 两虚证组(33例) ,测定并比较各组血脂指标 [ 总 胆固醇(TC)、三酰甘油(TG)]水平、血糖指标[空 腹血糖(FPG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)] 水平和 C反应蛋白(CRP)水平。采集各组患者空腹静脉血, 采用全自动生化分析仪(7600 型, 日立公司提供) 及配套试剂,采用酶法测定 TC、TG 水平,采用葡 糖氧化酶法测定 FPG(血浆血糖)水平,采用免疫 比浊法测定 CRP 水平;采用全自动糖化血红蛋白 分析仪(MQ-3000PT 型,上海惠中科技有限公司 提供)及配套试剂测定 HbA1c 水平(高效液相色 谱分析)。
1.3 观察指标 (1)观察 T2DM 患者不同中医证 型分布。(2) 比较各组 TC、TG、FPG、HbA1c、 CRP 水平。
1.4 统计学方法 应用 SPSS 22.0 软件进行统计学 分析,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,采用 t 检验,计数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,以 P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 300 例 T2DM 患者不同中医证型分布 300 例 T2DM 患者中,湿热困脾证占比最高为 39.00%, 其次为阴虚热盛证,占比为 21.00%,气阴两虚 证、血瘀脉络证、阴阳两虚证占比分别为 15.00%、 14.00%、11.00%。见表 1.
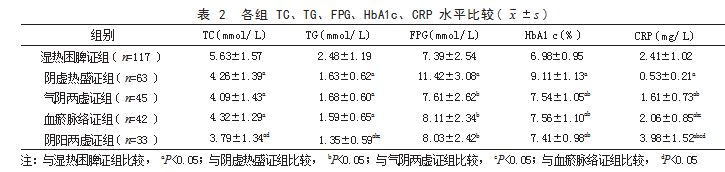
2.2 各 组 TC、TG、FPG、HbA1c、CRP 水 平 比 较 湿热困脾证组 TC、TG 水平高于阴虚热盛证组、 气阴两虚证组、血瘀脉络证组和阴阳两虚证组;阴 阳两虚证组 TC 水平低于血瘀脉络证组;阴阳两虚 证组 TG 水平低于阴虚热盛证组和气阴两虚证组, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。阴虚热盛证组 FPG 和 HbA1c 水平高于湿热困脾证组、气阴两虚 证组、血瘀脉络证组和阴阳两虚证组;湿热困脾证 组 HbA1c 水平低于气阴两虚证组、血瘀脉络证组 和阴阳两虚证组, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 阴阳两虚证组 CRP 水平高于湿热困脾证组、阴虚 热盛证组、气阴两虚证组和血瘀脉络证组;湿热 困脾证组 CRP 水平高于阴虚热盛证组、气阴两虚 证组和血瘀脉络证组;血瘀脉络证组 CRP 水平高 于阴虚热盛证组、气阴两虚证组;气阴两虚证组 CRP 水平高于阴虚热盛证组,差异均有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。见表 2.
3 讨论
中医体质学说认为,体质与机体的天赋与后天 诸多因素相互作用构成相对稳定的生理特点有关, 不同中医体质可影响疾病的发生、发展与转归 [6-8]。
临床针对 T2DM 病例,应充分考虑中医体质特征与 证候之间的关系,以提高 T2DM 患者的中医辨治 效果 [9-10]。
已知 T2DM 可引起血脂代谢紊乱,诱发一系列 心脑血管疾病 [11] 。本研究结果显示,湿热困脾证 组 TC、TG 水平高于阴虚热盛证组、气阴两虚证组、 血瘀脉络证组和阴阳两虚证组。这可能与现代社会 人们饮食结构中平素嗜食肥甘厚味、荤腥发物,脾 胃受损,中焦运化不利,水谷不能化为精微,聚湿 成痰,湿性黏腻,导致气郁化热、阻滞气机,导致 湿热困脾证有关。本研究结果同时显示,阴阳两虚 证组 TC 水平低于血瘀脉络证组;阴阳两虚证组 TG 水平低于阴虚热盛证组和气阴两虚证组。这可能与 阴阳两虚证患者病情已发展至糖尿病后期,病情复 杂,形体消瘦、津亏液耗有关 [12-13]。
本研究结果还显示,阴虚热盛证组 FPG、HbA1c 水平高于湿热困脾证组、气阴两虚证组、血瘀脉络证 组和阴阳两虚证组。分析原因为阴虚热盛证患者津液 耗伤严重,阴愈虚则热愈盛,热愈盛则益伤阴,糖代 谢紊乱严重,患者多饮、多尿症状表现明显,糖代 谢紊乱严重,故 FPG、HbA1c 水平升高。
已知 T2DM 作为一种炎性疾病。CRP 为常见炎 性指标, 可反映机体炎症反应程度 [14-15]。本研究结果 又显示,阴阳两虚证组 CRP 水平高于湿热困脾证组、 阴虚热盛证组、气阴两虚证组和血瘀脉络证组。这可 能与阴阳两虚证患者阴损及阳,肾阳衰微,肾失固摄 有关。因本研究中部分中医证型患者病例数较少,其 结果尚需增加样本量,开展深入研究予以印证。
综上所述,T2DM 患者的中医证型以湿热困脾 证为主, 其 TC、TG 水平较高,T2DM 阴虚热盛证 患者 FPG、HbA1c 水平较高,T2DM 阴阳两虚证患 者 CRP 水平较高。
参考文献
[1] 汪慧卉, 吴柱国, 王颖, 等 . 血清 YKL-40、CTRP-3 水平在2 型糖尿病心血管并发症中的诊断价值 [J]. 医学综述,2020. 26(8):1619-1623.
[2] 魏嘉 . 温通法治疗糖尿病偏身汗出一例 [J]. 环球中医药,2020.13(11):1970-1972.
[3] 邵正斌,黄平,夏铭蔚,等 . 300 例冠心病合并 2 型糖尿病患者中医证型与血脂、血糖和心脏超声结果的关系 [J]. 安徽中 医药大学学报,2019.38(4):36-39.
[4] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会 . 中国 2 型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2018.10(5):318-321.
[5] 中华医学会内分泌学分会 . 成人 2 型糖尿病胰岛素临床应用中国专家共识 [J]. 药品评价,2012.9(1):42-44.
[6] 王嘉祺,冯燕飞,张政,等 . 2 型糖尿病的中医证型和中医证素与西医指标的相关性分析 [J]. 中国医药导刊, 2020. 22(3):187-192.
[7] 浦莉俊 . 2 型糖尿病中医证型与糖、骨代谢主要实验室指标的相关性研究 [J]. 上海医药,2021.42(22):38-62.
[8] 赵灿,李娜,白秀伟,等 . 性别对 2 型糖尿病患者血糖控制水平与血脂相关性的影响 [J]. 河北医药,2019.41(3):414-417.
[9] 李伟露,李影 . 老年 T2DM 患者血清 CRP、尿微量白蛋白的水平及其与慢性血管并发症的关系 [J]. 海南医学,2019.30 (6):699-702.
[10] 代俊伟,唐晓磊 . 血清中 CysC、RBP、Hcy、CRP 水平与糖尿病肾病分期相关性研究 [J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2020. 40(3):385-388.
[11] 郝娟,段玉敏,郭晓宁 . 血清 CRP、Hcy 与糖尿病肾病患者尿白蛋白 / 肌酐比值的相关性及临床意义 [J]. 医学临床研究, 2019.36(6):1176-1178.
[12] 孙文早,李红玲,范丽娜,等 . 脂蛋白 a 和超敏 C 反应蛋白联合检测对糖尿病肾病早期诊断的临床价值 [J]. 医学研究杂 志,2019.48(2):155-157.
[13] 刘晓倩,金剑虹,王保法,等 . 2 型糖尿病合并肥胖患者的相关危险因素和中医证素分析 [J]. 世界科学技术 - 中医药现代 化,2021.23(9):3095-3101.
[14] 杨静,张卓然,李静,等 . 2 型糖尿病认知功能障碍病人的影响因素及中医证候分布特点研究 [J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病 杂志,2021.19(17):2917-2920.
[15] 冷雪,谷丽艳,朱芳 . 2 型糖尿病中医证型流行病学调查及其中医病因病机初探 [J]. 中华中医药杂志,2015.30(3):732-735.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网!
文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/yixuelunwen/60592.html