SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:分析开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的影响因素。方法: 采用便利抽样法选取 2021 年 9—12 月开封市养 老机构 480 名老年人作为研究对象,统计开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的现状,采用 Logistic 回归分析老年人群对医养结合养 老机构需求的影响因素。结果: 共发放 480 份问卷,回收有效问卷 454 份,根据是否对医养结合养老机构有需求分为有需求组(n=191)、 无需求组(n=263);有需求组年龄 <70 岁、衰弱程度中重度、医保类型城镇医疗保险、合并慢性疾病、抑郁程度中重度、生活自理能力 部分自理或失能、医养结合认知程度了解与熟悉、对养老机构印象较好占比均高于无需求组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);Logistic 回 归分析结果显示,年龄 <70 岁、衰弱程度中重度、医保类型城镇医疗保险、合并慢性疾病、抑郁程度中重度、生活自理能力部分自理或失 能、医养结合认知程度了解与熟悉、对养老机构印象较好均为开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的影响因素(OR>1. P<0.05)。 结论: 年龄 <70 岁、衰弱程度中重度、医保类型城镇医疗保险、合并慢性疾病、抑郁程度中重度、生活自理能力部分自理或失能、医养结 合认知程度了解与熟悉、对养老机构印象较好均为开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的影响因素。
Analysis ofinfluencingfactorsofKaifengelderlypopulation’sdemandforpension institutions of combination of medical and health care
PANG Yahui
(Kaifeng People’s Hospital, Kaifeng 475000 Henan, China)
【Abstract】 Objective:To analyze influencing factors of Kaifeng elderly population’s demand for pension institutions of combination of medical and health care. Methods:480 elderly people in the pension institutions in Kaifeng area from September to December 2021 were selected as the research objects by using the convenience sampling method. The status of the Kaifeng elderly population’s demand for the pension institutions of combination of medical and health care was statistically analyzed. Logistic regression was used to analyze the influencing factors of the elderly population’s demand for the pension institutions of combination of medical and health care. Results:480 questionnaires were distributed and 454 valid questionnaires were collected. According to whether there is a demand for pension institutions of combination of medical and health care, they were divided into demand group (n=191) and non-demand group (n=263). The proportions of the elderly population with age < 70 years old, moderate to severe degree of frailty, medical insurance type of urban medical insurance, combined chronic diseases, moderate to severe depression, partial self-care or disability of self-care ability, understanding and familiarity of the combination of medical and health care, and good impression of pension institutions in the demand group were higher than those in the non-demand group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that age < 70 years old, moderate to severe degree of frailty, type of urban medical insurance, chronic diseases, moderate to severe degree of depression, partial self-care or disability of self- care ability, understanding and familiarity of the combination of medical and health care, and good impression of pension institutions were the influencing factors of Kaifeng elderly population’s demand for the pension institutions of combination of medical and health care (OR> 1. P<0.05). Conclusions:Age < 70 years old, moderate to severe degree of frailty, type of urban medical insurance, chronic diseases, moderate to severe degree of depression,partial self-care or disability of self-care ability, understanding and familiarity of the combination of medical and health care, and good impression of pension institutions are the influencing factors of Kaifeng elderly population’s demand for the pension institutions of combination of medical and health care
【Keywords】 Elderly population; Combination of medical and health care; Pension institution; Demand; Influencing factor
随着我国老龄化日趋严重,需要照料的失能、 半失能老年人养老问题日益凸显,传统居家养老已无法满足当今老年人的生活需求 [1-2]。现有养老机 构不能同时满足医疗服务与养老服务 [3]。医养结合 养老机构是由生活照料、康复、医疗及护理等多元 素组成,构建新型养老模式,可为老人提供有效疾 病医疗和专业化服务,做到有病治病、无病养老[4-5]。本文分析开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求 的影响因素。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 采用便利抽样法选取 2021 年 9— 12 月开封市养老机构 480 名老年人作为研究对象。 纳入标准:属于开封市地区常住居民,居住年限≥ 3 年;年龄≥ 60 岁;有正常语言沟通、理解能力 及行为能力。排除标准:恶性肿瘤;不能配合完成 调查研究。所有研究对象对本研究内容了解并自愿 签署知情同意书。
1.2 方法 采用本院自制一般资料调查问卷开展 调查,主要内容为性别、年龄、文化程度、婚姻状 况、退休前职业、个人月平均收入、子女个数、衰 弱程度、照料来源、居住方式、医保类型、健康自 评、是否合并慢性疾病、抑郁程度、生活自理能力、 医养结合认知程度、对养老机构印象。采用抑郁自 评量表(SDS) 评估老年人抑郁程度, 共计 20 个条 目,总分 80 分,根据评分分为重度(SDS 评分≥ 73 分)、中度(63 分≤ SDS 评分≤ 72 分)、轻度 (53 分≤ SDS评分≤ 62分)、无(SDS评分<53分)。 该量表 Cronbach’α 为 0.784.采用衰弱综合评估 量表(CFAI)评估老年人身体衰弱情况,共 23 个 条目,得分与衰弱程度呈正相关,根据评分结果分 为轻度衰弱(20~40 分)、中度衰弱(41~50 分)、 重度衰弱(51~97 分)。质量控制:由医院选取医生、护士担任调查员 开展问卷调查,调查员均接受统一规范培训,考核 合格才能参与现场调查, 且现场调查均设有质控员, 采用双人双录入进行后期数据录入。共调查 480 名 开封市地区常住人口,应答率为 94.58%,有效调 查 454 名。
1.3 观察指标 (1)统计开封市老年人群对医养 结合养老机构需求的现状。(2)开封市老年人群 对医养结合养老机构需求的单因素分析。(3)采 用 Logistic 回归分析开封市老年人群对医养结合养 老机构需求的影响因素。
1.4 统计学方法 采用 SPSS 20.0 统计软件处理数据,计量资料以(x(—) ±s )表示,比较采用 t 检验,计数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,多因素分 析采用 Logistic 回归分析, 以 P<0.05 为差异有统计 学意义。
2 结果
2.1 开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的现状 454 名养老机构的老年人中,对医养结合养 老机构有需求 191 名,对医养结合养老机构无需求 263 名。 根据是否对医养结合养老机构有需求分为 有需求组( n=191)、无需求组( n=263)。
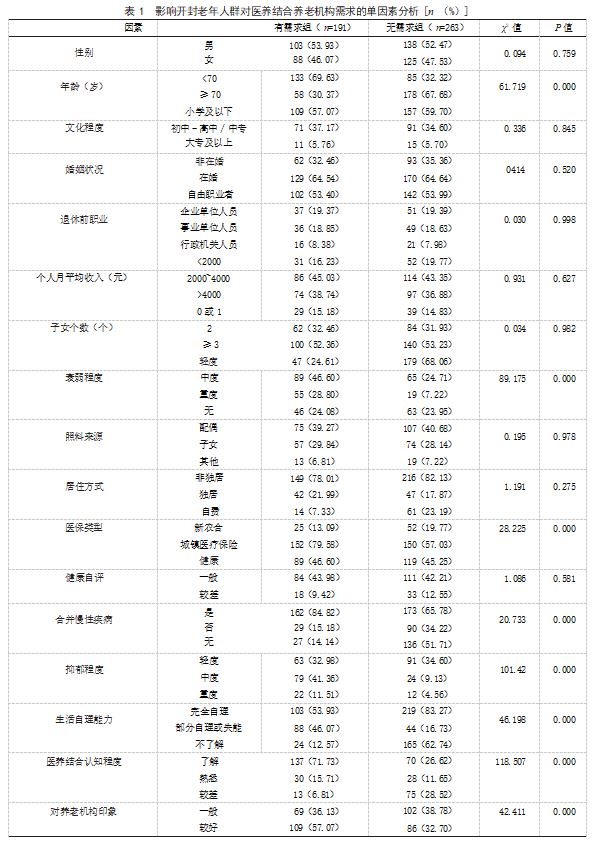
2.2 老年人对医养结合养老机构需求的单因素分 析 两组性别、文化程度、婚姻状况、退休前职业、 个人月平均收入、子女个数、照料来源、居住方式、 健康自评情况比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 有需求组年龄 <70 岁、衰弱程度中重度、医保类型 城镇医疗保险、合并慢性疾病、抑郁程度中重度、 生活自理能力部分自理或失能、医养结合认知程度 了解与熟悉、对养老机构印象较好占比均高于无需 求组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表 1.
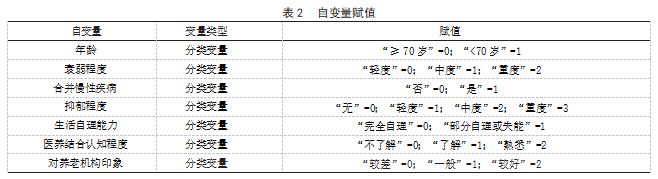
2.3 开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的 影响因素分析 以有无医养结合养老结构需求为因 变量,以年龄、衰弱程度、医保类型、合并慢性疾 病、抑郁程度、生活自理能力、医养结合认知程度、 对养老机构印象为自变量并赋值,见表 2.Logistic 回归分析结果显示, 年龄 <70 岁、衰弱程度中重度、 医保类型城镇医疗保险、合并慢性疾病、抑郁程度 中重度、生活自理能力部分自理或失能、医养结合 认知程度了解与熟悉、对养老机构印象较好均为开 封市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的影响因素(OR>1. P<0.05)。见表 3.
3 讨论
已知我国 60 岁以上老年人占总人数的 17.3%, 失能、半失能老年人高达 4000 万 [6-7]。医养结合养 老机构可弥补传统养老机构的不足,开展专业医护 服务,实现多方共赢 [8-9]。
本研究 Logistic 回归分析结果显示,年龄 <70 岁、 衰弱程度中重度、医保类型城镇医疗保险、合并慢 性疾病、抑郁程度中重度、生活自理能力部分自理 或失能、医养结合认知程度了解与熟悉、对养老机 构印象较好均为开封市老年人群对医养结合养老机 构需求的影响因素。分析原因:(1)年龄 <70 岁。 高龄老人常回忆过去,怀念自己生长、生活的家 庭,致使高龄老人晚年更想回归家庭。因此养老护 理人员应加强对高龄老人的心理疏导,增强其自身 认同感,打破老人传统观念束缚 [10]。(2) 合并慢 性疾病、生活自理能力部分自理或失能。慢性疾病 会引起老年人身体诸多不便,进而增加对医疗保健 服务的需求,医养结合养老机构可提供针对性养老 照护服务 [11]。(3) 衰弱中重度、抑郁程度中重度。
随着年龄增长,衰弱程度加深,常需要医养结合养 老机构为其提供全方位养老照护服务,另在疾病及 孤单、失落等心理因素的双重作用下,老年人心理 抑郁程度不断加深,呈现出更高的医养结合养老需 求 [12-13]。(4)对养老机构印象较好、医养结合认 知程度了解与熟悉。医养结合养老机构是一种新型 养老模式,现阶段医养结合机构养老还未达到老年 人的真正养老需求,老年人认知层面还停留在传统 养老机构,因而对于选择医养结合机构养老的积极 性不高 [14]。
综上可知,年龄 <70 岁、衰弱程度中重度、医 保类型城镇医疗保险、合并慢性疾病、抑郁程度中 重度、生活自理能力部分自理或失能、医养结合认 知程度了解与熟悉、对养老机构印象较好均为开封 市老年人群对医养结合养老机构需求的影响因素。
参考文献
[1] 沈珵,王娜娜,刘佩玉,等 . 基于社区居家养老视角对 120 例失能老人护理需求的调查研究 [J]. 重庆医学, 2020.49(9): 1520-1524.
[2] 原温佩,薛雅卿,蔡圆,等 . 老年人多重慢病患病现状及生 活自理能力调查 [J]. 现代预防医学,2021.48( 14): 2590- 2593.
[3] 杨娟,郑晓,候丽红,等 . 太原市老年人多重慢病患病现状 及影响因素 [J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021.25( 1): 78-83.
[4] 赵旻,王亚楠,姜亚芳,等 . 医养结合背景下社区老年人居家护理服务需求现状调查研究 [J]. 护理管理杂志,2020.20 (8): 540-543.
[5] 陈冰洁,窦丽,韩雯雯,等 . 乌鲁木齐市医养结合型养老机 构养老护理员核心胜任力现状及影响因素分析 [J]. 中国医药 导报, 2020.17(34): 8-11.
[6] 施小明 . 新形势下我国老年人口面临的主要公共卫生挑战 [J]. 中华医学杂志, 2021.101(44): 3613-3619.
[7] 朱春燕,郭晴, 田庆丰,等 . 河南省老年人综合能力失能 现况及影响因素研究 [J]. 中国全科医学,2021.24( 12): 1500-1505.
[8] 刘洪章,李梦莎,陈冬冬,等 . 合肥市医养结合机构入住老 年人服务满意度调查 [J]. 安徽医学,2020.41(2): 218- 221.
[9] 张玉杰,尹文强,闫语,等 . 居民对医养结合养老服务参与 意愿的 Meta 分析 [J]. 中国全科医学, 2022.25( 10): 1269- 1274.
[10] 王彬丁,刘刚,郑新烈,等 . 医养结合养老机构老年人日常 生活活动需求未满足状况及影响因素研究 [J]. 中国全科医学, 2021.24( 19): 2465-2471.
[11] 伍丽群,姚克勤,李刚,等 . 深圳市老年人医养结合照护需求 及其影响因素 [J]. 中国公共卫生, 2020.36(4): 529-532.
[12] 侯晓琳,高静,吴晨曦,等 . 养老机构老年人衰弱现状及分 析 [J]. 中华护理杂志, 2018.53( 1): 88-93.
[13] 刘硕,朱鸣雷,刘晓红,等 . 老年住院患者衰弱和抑郁的相 关性 [J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2020.19(6): 419- 423.
[14] 吴丽娟,廖少玲,文若兰,等 . 湛江市城区老年人医养结合 需求及影响因素分析 [J]. 护理研究, 2019.33( 1): 10-13.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网!
文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/yixuelunwen/70318.html