SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:分析 97 例学龄期单眼屈光参差性弱视患儿的频域光学相干断层扫描(SD-OCT)参数。方法: 选取 2019 年 10 月 至 2021 年 6 月该院收治的 97 例学龄期单眼屈光参差性弱视患儿进行前瞻性研究,根据不同屈光参差性弱视类型,将弱视患儿分为远视组 ( n=56) 和近视组( n=41) 。对患儿两眼进行 SD-OCT 检查,比较患儿双侧眼睛以及远视组和近视组组间 SD-OCT 参数(黄斑中心凹、内 环上方、内环颞侧、内环下方、内环鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、外环下方、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视网膜厚度) 。结果: 患侧眼内环上方、 内环颞侧、内环鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、外环下方等黄斑区视网膜厚度均厚于健侧眼,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 患侧眼和健侧 眼的黄斑中心凹、内环下方、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视网膜厚度比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05) ;远视组内环下方、内环鼻侧、外环上方、 外环颞侧、外环下方等黄斑区视网膜厚度均薄于近视组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05) ;远视组和近视组黄斑中心凹、内环上方、内环颞 侧、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视网膜厚度比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:学龄期单眼屈光参差性弱视患儿患侧眼内环上方、内环颞侧、 内环鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、外环下方等区域的 SD-OCT 参数水平均增高, 且远视与近视患儿黄斑视网膜 SD-OCT 参数水平存在差异。
Analysis of SD-OCT parameter of 97 school-age children with monocular anisometropic amblyopia
XIE Yuanchun
(Children’s Hospital Affiliated to Zhengzhou University, Henan Children’s Hospital, Zhengzhou Children’s Hospital,
Zhengzhou 450000 Henan, China)
【Abstract 】 Objective: To analyze frequency domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) parameters of 97 school-age children with monocular anisometropic amblyopia. Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 97 school-age children with monocular anisometropic amblyopia admitted to this hospital from October 2019 to June 2021. The affected eye was set as amblyopia group (n=97), and the healthy eye was set as control group (n=97). According to different types of anisometropic amblyopia, the amblyopic group was divided into hyperopia group (n=56) and myopia group (n=41). SD-OCT was performed on both eyes of these children. The SD-OCT parameters (retinal thickness levels of macular central fovea, upper side of inner ring, temporal side of inner ring, lower side of inner ring, nasal side of inner ring, upper side of outer ring, temporal side of outer ring, lower side of outer ring, nasal side of outer ring) were compared between the amblyopia group and the control group and between the hyperopia group and the myopia group. Results: The retinal thickness levels of the macular area above the inner ring, the temporal side of the inner ring, the nasal side of the inner ring, the upper side of the outer ring, the temporal side of the outer ring, and the lower side of the outer ring in the amblyopia group were thicker than those in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in the macular retinal thickness levels of the macular central fovea, the lower side of inner ring and the nasal side of outer ring between the amblyopic group and the control group (P>0.05). The macular retinal thickness in the lower side of the inner ring, the nasal side of the inner ring, the upper side of the outer ring, the temporal side of the outer ring and the lower side of the outer ring in the hyperopia group were thinner than those in the myopia group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There were no significant differences in the macular retinal thickness levels of the macular central fovea, the upper side of inner ring, the temporal side of inner ring and the nasal side of outer ring between the hyperopia group and the myopia group (P>0.05). Conclusions: The school-age children with monocular anisometropic amblyopia have increased SD-OCT parameters such as macular retinal thickness in the upper side of inner ring, the temporal side of the inner ring, the nasal side of the inner ring, the upper side of outer ring, the temporal side of the outer ring, and the lower side of outer ring. There were differences in the SD-OCT parameters of macular retina between the hyperopia and myopic school-age children with monocular anisometropic amblyopia.
【Keywords】 School age; Monocular; Anisometropic amblyopia; Frequency domain optical coherence tomography; Macula lutea; Retinal thickness
弱视包括屈光参差性弱视、屈光不正性弱视、斜视性弱视等 [1-2]。已知弱视患者可存在视网膜组 织结构异常 [3]。本文分析 97 例学龄期单眼屈光参 差性弱视患儿频域光学相干断层扫描(SD-OCT) 参数,为临床诊疗提供参考。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2019 年 10 月至 2021 年 6 月 本院收治的 97 例学龄期单眼屈光参差性弱视患儿 进行前瞻性研究。纳入标准:符合单眼屈光参差性 弱视诊断标准 [4] ;无斜视;对侧眼视力正常,最佳 矫正视力≥ 1.0.排除标准:眼部手术史;有 SD- OCT 检查禁忌证。患儿家长对本研究内容了解且自 愿签署知情同意书,研究经本院伦理委员会审批通 过。97 例学龄期单眼屈光参差性弱视患儿中男 49 例, 女 48 例; 年龄 6~12 岁, 平均(9.15±1.24)岁。 根据不同弱视类型,将患儿分为远视组( n=56) 和 近视组( n=41)。
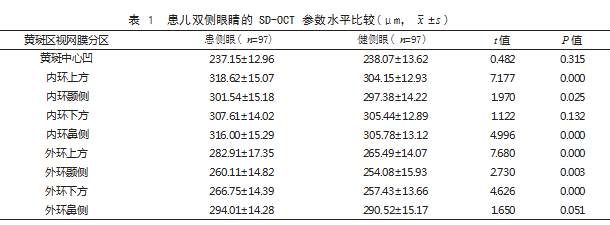
1.2 方法 使用 optovue 光学相干断层扫描仪(光 视)对患儿两眼进行检查。首先对患儿进行散瞳, 至瞳孔直径 >6 mm,坐位状态下,使用内注视法, 采用 Macular Cube 512×128 扫描模式, 获取患儿 黄斑区信息。将黄斑中心凹作为中心,然后分别进 行直径为 1、3、6 mm 的线性扫描, 放射状线性扫 描共 6 条,两条线夹角为 30°,行相同参数扫描, 获取黄斑区视网膜厚度,并绘制出伪彩色黄斑地形 图。根据 ETDRS 标准将所有患儿黄斑分为黄斑中 心凹区、内环上方、内环颞侧、内环下方、内环鼻 侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、外环下方、外环鼻侧。
1.3 观察指标 (1)比较患儿双侧眼睛的 SD- OCT 参数水平,包括黄斑中心凹、内环上方、内环 颞侧、内环下方、内环鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、 外环下方、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视网膜厚度。各区划 分见图 1.(2)比较远视组和近视组 SD-OCT 参 数水平, 包括黄斑中心凹、内环上方、内环颞侧、 内环下方、内环鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、外环 下方、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视网膜厚度。
1.4 统计学方法 应用 SPSS 22.0 软件进行统计学 分析,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,采用 t 检验,计数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,以 P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 患儿双侧眼睛 SD-OCT 参数水平比较 患侧 眼内环上方、内环颞侧、内环鼻侧、外环上方、外 环颞侧、外环下方等黄斑区视网膜厚度均厚于健侧 眼, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 患侧眼和健侧 眼的黄斑中心凹、内环下方、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视 网膜厚度比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见 表 1.
2.2 远视组和近视组 SD-OCT 参数水平比较 远 视组内环下方、内环鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、 外环下方等黄斑区视网膜厚度均薄于近视组,差异 有统计学意义(P<0.05) ;远视组和近视组黄斑中 心凹、内环上方、内环颞侧、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视 网膜厚度比较, 差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见 表 2.
3 讨论
屈光参差性弱视指两眼屈光度不等(柱镜度 之差≥ 1.00 D,球镜度之差≥ 1.50 D)的弱视 [5-6]。
光学相干断层扫描(OCT)可有效分辨视网膜神经 纤维层视网膜微细结构, 反映视网膜形态学改变 [7]。 SD-OCT 为新一代 OCT 扫描技术,具有技术参数更 加完善、分辨率高、扫描速度快等优势 [8] ,可实现 对视网膜厚度快速、可重复性扫描测量,提高结果 准确性 [9-10]。
本研究结果显示, 患侧眼内环上方、内环颞侧、 内环鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、外环下方等黄斑 区视网膜厚度均厚于健侧眼;患侧眼和健侧眼的黄 斑中心凹、内环下方、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视网膜厚 度比较,差异无统计学意义。提示学龄期单眼屈光 参差性弱视患儿患眼黄斑视网膜区厚度发生改变, 且具有区域差异。分析原因为弱视眼黄斑中心凹早 期未能得到足够的视觉刺激,可引起黄斑区视网膜 发育受阻 [11-13]。
本研究结果同时显示,远视组内环下方、内环 鼻侧、外环上方、外环颞侧、外环下方等黄斑区视 网膜厚度均薄于近视组;远视组和近视组黄斑中心 凹、内环上方、内环颞侧、外环鼻侧等黄斑区视网 膜厚度比较,差异无统计学意义。提示不同类型学 龄期单眼屈光参差性弱视患儿黄斑视网膜厚度改变 存在差异。分析原因可能与近视屈光参差性弱视患 儿的眼轴较长,远视屈光参差性弱视患儿的眼轴较 短有关 [14-15]。
综上所述,学龄期单眼屈光参差性弱视患儿的 患侧眼内环上方、内环颞侧、内环鼻侧、外环上方、 外环颞侧、外环下方等区域的 SD-OCT 参数水平均 增高,且远视与近视患儿黄斑区视网膜 SD-OCT 参 数水平存在差异。
参考文献
[1] 甘露,蓝方方,赵武校,等 . 不同程度远视屈光参差性弱视的波前像差特点 [J]. 国际眼科杂志,2019.19(3):446-449.
[2] 项潇琼,罗丽颖,唐敏,等 . 光学相干断层扫描血管成像在屈光参差性弱视儿童中的应用 [J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学 版),2019.39(1):79-83.
[3] 李博,王星,尹曦敏,等 . 弱视眼视网膜改变的研究进展 [J].广西医学,2019.41(1):83-85.
[4] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会 . 弱视诊治指南 [J]. 中国实用乡村医生杂志,2019.26(2):3-5.
[5] 董玉红,霍敏,张静 . 硬性透氧性角膜接触镜对单眼屈光参差性弱视儿童的矫治效果观察 [J]. 安徽医药, 2019. 23(3) :510-512.
[6] 赵博文,付晶,于静,等 . 屈光参差性弱视儿童短期单纯屈光矫正疗效分析 [J]. 中国斜视与小儿眼科杂志, 2019. 27(2):5-8.
[7] 李红阳,黎燕英,薛丽萍,等 . 手持式视网膜视力计、光学相干断层成像技术对白内障合并黄斑前膜患者的术后视力预 测 [J]. 南方医科大学学报,2021.41(1):123-127.
[8] 彭红娟, 方林彬, 郑彪 . 基于频域光学相干断层扫描 (SD-OCT)的视盘周围视网膜总厚度在早期视盘水肿诊断中的应用 [J]. 眼科新进展,2020.40(1):42-45.
[9] 刘贤洁,陈禹橦,刘美丹,等 . 应用频域光学相干断层扫描分析高度近视患者黄斑区外层视网膜厚度 [J]. 中国医科大学 学报,2018.47(5):390-393.
[10] 郑磊,张国明,孙良南,等 . 基于 SD-OCT 建立新的前膜分级法评估 IMEM 对年龄相关性白内障患者术后视功能的影 响 [J]. 国际眼科杂志,2021.21(6):980-985.
[11] 刘华,许多,陈宇,等 . 不同类型弱视儿童视网膜结构和视觉诱发电位及立体视功能的差异性分析 [J]. 国际眼科杂志, 2020.20(4):688-691.
[12] 吴杨杨,罗红,李艽 . 单眼屈光参差性弱视黄斑区及视盘周围神经纤维层厚度的 Meta 分析 [J]. 国际眼科杂志,2020.20 (9):1560-1566.
[13] 张荻,陶思羽,李舒茵,等 . 屈光参差性弱视眼黄斑频域光学相干断层成像研究 [J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016. 30(9):897-899.
[14] 陈嘉锡,何花 . 远视屈光参差性弱视患儿视网膜结构学研究 [J]. 中国斜视与小儿眼科杂志,2019.27(1):15-19.
[15] 夏哲人,周襄沅,陈豪,等 . 屈光参差性弱视儿童黄斑厚度与视盘周围视网膜神经纤维层厚度的相关性分析 [J]. 浙江医 学,2019.41 (3): 246-250.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网!
文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/yixuelunwen/62479.html