SCI论文(www.lunwensci.com)
【摘要】 目的:观察戊酸雌二醇联合黄体酮胶囊治疗无排卵型月经不调患者的效果。方法: 选取 2019 年 5 月至 2020 年 10 月该院 收治的 94 例无排卵型月经不调患者进行前瞻性研究。按照随机数字表法分为对照组和观察组各 47 例。两组均给予常规治疗, 在此基础上, 对照组予以戊酸雌二醇治疗,观察组予以戊酸雌二醇联合黄体酮胶囊治疗。比较两组疗效、月经时长、月经周期、子宫内膜厚度、血清性 激素 [ 孕酮(P)、雌二醇(E2 )、促卵泡成熟激素(FSH) ] 水平、卵泡发育指标(卵泡直径、优质卵泡数) 水平和不良反应发生率。 结果: 治疗后,两组月经时长、月经周期均短于治疗前,且观察组短于对照组,两组子宫内膜厚度均低于治疗前,且观察组低于对照组,差异有 统计学意义(P<0.05) ;治疗后,两组 FSH 水平均低于治疗前,且观察组低于对照组,两组 E2、P 水平均高于治疗前,且观察组高于对照 组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05) ;治疗后,两组卵泡直径均大于治疗前,且观察组大于对照组,两组优质卵泡数均多于治疗前,且观察 组多于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05) ;观察组不良反应发生率为 10.64%,对照组不良反应发生率为 8.51%,两组不良反应发生率 比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论: 戊酸雌二醇联合黄体酮胶囊治疗无排卵型月经不调患者可提高治疗总有效率及 E2、P 和卵泡 发育指标水平,缩短月经时长和月经周期,降低子宫内膜厚度和 FSH 水平,优于单纯戊酸雌二醇治疗效果。
【关键词】 戊酸雌二醇,黄体酮胶囊,无排卵型月经不调,卵泡发育,子宫内膜,不良反应
Effects of Estradiol valerate combined with Progesterone capsules in treatment of patients with anovulatory irregular menstruation
LI Zhan
(General Gynecology of Zhumadian Central Hospital, Zhumadian 463000 Henan, China)
【Abstract 】 Objective: To observe effects of Estradiol valerate combined with Progesterone capsules in treatment of patients with anovulatory irregular menstruation. Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 94 patients with anovulatory irregular menstruation admitted to the hospital from May 2019 to October 2020. According to random number table method, they were divided into control group and observation group, 47 cases in each group. Both groups were given routine treatment. On this basis, the control group was treated with Estradiol valerate, while the observation group was treated with Estradiol valerate combined with Progesterone capsules. The efficacy, the menstrual duration, the menstrual cycle, the endometrial thickness, the serum sex hormone levels [progesterone (P), estradiol (E2), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)], the follicular development indicator levels (follicle diameter, number of high-quality follicles), and incidence of adverse reactions were compared between the two groups. Results: After the treatment, the menstrual duration and the menstrual cycle of the two groups were shorter than those before the treatment, and those in the observation group were shorter than those in the control group; the endometrial thickness of the two groups was thinner than that before the treatment, and that in the observation group was thinner than that in the control group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After the treatment, the FSH levels of the two groups were lower than those before the treatment, and that of the observation group was lower than that of the control group; the levels of E2 and P in the two groups were higher than those before the treatment, and those in the observation group were higher than those in the control group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After the treatment, the follicle diameter of the two groups was larger than that before the treatment, and that in the observation group was larger than that in the control group; the numbers of high-quality follicles in both groups were more than those before the treatment, and that of observation group was more than that of the control group; and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Further, the incidence of adverse reactions was 10.64% in the observation group and 8.51% in the control group, and the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05). Conclusions: Estradiol valerate combined with Progesterone capsules in the treatment of the patients with anovulatory irregular menstruation can improve the total effective rate and the levels of E2. P and follicular development indexes, shorten the menstrual duration and the menstrual cycle, and reduce the endometrial thickness and the FSH levels. Moreover, it is superior to single Estradiol valerate treatment.
【Keywords】 Estradiol valerate; Progesterone capsules; Anovulatory irregular menstruation; Follicular development; Endometrium; Adverse reaction
无排卵型月经不调由神经内分泌功能障碍诱 发,可导致雄激素水平升高、月经紊乱、排卵障碍 等症状,严重时可导致不孕不育 [1-2] 。目前临床常 采用性激素治疗该病,戊酸雌二醇可反馈调节下丘 脑 - 腺垂体, 增加子宫内膜厚度, 改善黄体功能 [3]。 黄体酮对保护子宫内膜、止血具有重要意义 [4] 。本 文观察戊酸雌二醇联合黄体酮胶囊治疗无排卵型月 经不调患者的效果。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取 2019 年 5 月至 2020 年 10 月 该院收治的 94 例无排卵型月经不调患者进行前瞻 性研究。纳入标准:符合《妇产科学》[5] 中无排卵 型月经不调诊断标准;经 B 超检查确诊。排除标准: 严重肝肾功能障碍;合并子宫内膜异位症;存在子 宫肌瘤、垂体肿瘤;伴有血液系统、代谢疾病;对 本研究所用药物过敏。患者对本研究内容了解并自 愿签署知情同意书,且研究经本院伦理委员会审核 通过(批准文号:2019-07-006)。按照随机数字 表法分为对照组和观察组各 47 例。对照组:年龄 20~31 岁, 平均(26.36±2.20) 岁; 病程 2~12 个 月, 平均(4.37±1.63) 个月; 体质量 45~74 kg, 平均(60.13±6.97)kg。观察组: 年龄 21~30 岁, 平 均(25.41±2.46) 岁; 病 程 2~11 个 月, 平 均 (4.26±1.49) 个 月; 体 质 量 46~74 kg, 平 均 (60.24±6.85)kg。两组一般资料比较, 差异无统 计学意义(P>0.05),有可比性。
1.2 方法 两组治疗期间均禁止坐浴、性生活、 使用其他抗生素类药物。在此基础上,对照组采用 戊酸雌二醇(Jenapharm GmbH & Co.KG,国药准字 J20171038.1 mg) 口服治疗, 于月经周期第 5 天 开始服用,2 mg/ 次,1 次 /d。
观察组在对照组基础上联合黄体酮胶囊(浙 江仙琚制药股份有限公司,国药准字 H20041902. 50 mg)口服治疗,于月经周期最后 10 d 开始服用, 100 mg/ 次,1 次 /d。两组均连续治疗 3 个周期。 1.3 观察指标 (1)比较两组疗效。显效:停药 后子宫内膜厚度、月经均恢复正常;有效:子宫内 膜厚度未恢复正常,月经有所改善,但未达到正 常情况;无效:子宫内膜厚度无变化,无月经出 现。总有效率 = 显效率 + 有效率。(2)比较两组 治疗前后月经时长、月经周期、子宫内膜厚度。采 用阴道彩超仪(美国 GE 公司,型号:voluson E8) 检测子宫内膜厚度。(3)比较两组治疗前后血清性激素指标水平。采集患者清晨空腹静脉血 5 mL, 3000 r/min 转速(离心半径 10 cm), 离心 5 min, 取上清液,采用电化学发光法测定孕酮(P) 、雌 二醇(E2 ) 、促卵泡成熟激素(FSH) 水平。(4) 比较两组治疗前后卵泡发育指标水平。采用阴道彩 超仪(美国 GE 公司,型号:voluson E8)检测卵泡 直径、优质卵泡数。(5)比较两组不良反应发生率。 1.4 统计学方法 采用 SPSS 22.0 统计学软件处理 数据,计量资料以( x(—) ±s )表示,采用 t 检验,计 数资料以率(%)表示,采用 χ2 检验,以 P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
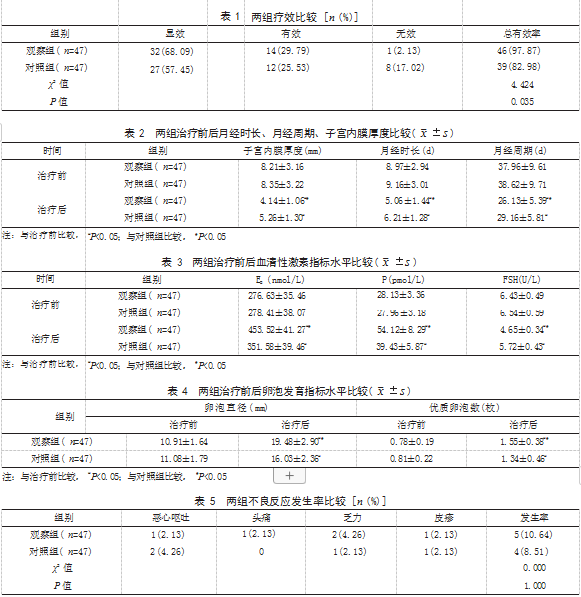
2.1 两组疗效比较 观察组治疗总有效率为 97.87%,高于对照组的 82.98%,差异有统计学意 义(P<0.05)。见表 1.
2.2 两组月经时长、月经周期、子宫内膜厚度比 较 治疗前,两组月经时长、子宫内膜厚度、月经 周期比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05); 治疗 后,两组月经时长、月经周期均短于治疗前,且 观察组短于对照组,两组子宫内膜厚度均低于治 疗前,且观察组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。见表 2.
2.3 两组治疗前后血清性激素指标水平比较 治 疗前,两组 E2、P、FSH 水平比较,差异均无统计 学意义(P>0.05) ;治疗后, 两组 FSH 水平均低于 治疗前,且观察组低于对照组,两组 E2、P 水平均 高于治疗前,且观察组高于对照组,差异有统计学 意义(P<0.05)。见表 3.
2.4 两组治疗前后卵泡发育指标水平比较 治疗 前,两组卵泡直径、优质卵泡数比较,差异均无统 计学意义(P>0.05) ;治疗后,两组卵泡直径均大 于治疗前,且观察组大于对照组,两组优质卵泡数 均多于治疗前,且观察组多于对照组,差异有统计 学意义(P<0.05)。见表 4.
2.5 两组不良反应发生率比较 观察组不良反应 发生率为 10.64%, 对照组不良反应发生率为8.51%, 两组不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意义 ( P>0.05)。见表 5.
3 讨论
女性月经周期可因情绪波动、长期生活不规律、 寒冷刺激、孕激素缺乏等因素而影响子宫内膜螺旋 动脉发育、生长,从而诱发无排卵型月经不调 [6-8], 且可增加子宫内膜癌发生风险 [9]。戊酸雌二醇片可促进受损子宫内膜的修复,且不良反应发生率较 低 [10]。黄体酮可促进子宫黏膜内腺体的生长, 与雌 激素协同还可改善月经周期,且黄体酮胶囊对肝肾 功能损伤较小, 安全性高 [11]。本研究结果显示, 观 察组治疗总有效率高于对照组;治疗后,观察组月 经时长、月经周期均短于对照组,子宫内膜厚度、 FSH 水平均低于对照组,E2、P 水平均高于对照 组,卵泡直径均大于对照组,优质卵泡数均多于对 照组;两组不良反应发生率比较,差异无统计学意 义。提示,戊酸雌二醇联合黄体酮胶囊治疗无排卵 型月经不调患者效果显著。分析原因为戊酸雌二醇 可加速子宫内膜创面修复,黄体酮胶囊可促进子宫内膜生长,两药合用可发挥协同增效作用 [12-13] 。本 研究结果还显示,两组不良反应发生率比较,差异 无统计学意义。提示联合黄体酮胶囊用药未增加安 全风险。
综上所述,戊酸雌二醇联合黄体酮胶囊治疗无 排卵型月经不调患者可提高治疗总有效率及 E2、P 和卵泡发育指标水平,缩短月经时长和月经周期, 降低子宫内膜厚度和 FSH 水平,优于单纯戊酸雌 二醇治疗效果。
参考文献
[1] 周丽霞,肖琳 . 口服黄体酮胶囊联合雌激素注射治疗子宫异 常出血疗效 [J]. 中国计划生育学杂志,2020.8(6):70-72.
[2] 欧艳,蒋海微 . 不同剂量黄体酮胶囊联合桂枝茯苓丸治疗无排卵型月经不调疗效观察 [J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2020.35(19):3669-3671.
[3] 金吉如 . 戊酸雌二醇片联合黄体酮胶囊及更年安片对 PPS 患者 FSH、LH、E2 及骨密度水平的影响 [J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2020.35(18):114-116.
[4] 刘燕华,刘嵩峰 . 探讨分析在治疗无排卵型的月经失调患者中应用不同黄体酮剂量临床的治疗效果 [J]. 中国妇产科临床 杂志,2020.21(1):85-86.
[5] 曹泽毅 . 中华妇产科学 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2014:16-23.
[6] De Souza MJ,Mallinson RJ,Strock NCA, et al. Randomised controlled trial of the effects of increased energy intake on menstrual recovery in exercising women with menstrual disturbances: the 'REFUEL’ study[J]. Hum Reprod,2021.36(8):2285-2297.
[7] 金雪静,盛祝梅,张治芬 . 青春期排卵障碍型异常子宫出血的诊断与治疗 [J]. 中国计划生育和妇产科,2019.11(11):17-18.
[8] Zhou X,Yang X. Association between obesity and oligomenorrhea or irregular menstruation in Chinese women of childbearing age:a cross-sectional study[J]. Gynecol Endocrinol,2020.36(12):1101-1105.
[9] 李晨辉,吴永平,谢芳,等 . 耳穴贴压联合针灸辅助激素治疗月经不调临床研究 [J]. 陕西中医,2020.41(3):387-389.
[10] 王婧婧,王张 . 调经赞育丸对戊酸雌二醇诱导的大鼠无排卵型功能失调性子宫出血的改善作用 [J]. 现代药物与临床, 2019.34(4):955-959.
[11] 柳书勤,殷敏敏,齐继红,等 . 益妇止血丸联合黄体酮治疗无排卵型功能失调性子宫出血的临床研究 [J]. 现代药物与临 床,2019.34(11):3399-3403.
[12] 陈晨,邢宇瑞,王晓霞,等 . 戊酸雌二醇联合屈螺酮炔雌醇片治疗无排卵型功能失调性子宫出血患者的效果及对子宫内 膜厚度的影响 [J]. 中国医学工程,2022.30(1):112-114.
[13] 李晓岚,梁小娟,陈小宁 . 戊酸雌二醇分别与黄体酮胶囊、醋酸甲羟孕酮联合治疗无排卵性功血对月经周期、疗效及不良反 应影响 [J]. 医学理论与实践,2017.30(24):3684-3685.
关注SCI论文创作发表,寻求SCI论文修改润色、SCI论文代发表等服务支撑,请锁定SCI论文网!
文章出自SCI论文网转载请注明出处:https://www.lunwensci.com/ligonglunwen/57258.html